Chemical Weathering Drawing, Web chemical weathering involves the chemical transformation of minerals and commonly results in the dissolution of minerals in a rock.
Chemical Weathering Drawing - Web chemical weathering is the process by which rocks are decomposed by chemical processes like hydration, reduction, oxidation, carbonation, etc. Different types of rocks weather at different rates. Rocks are dissolved or reduced to a fine condition by chemical weathering processes like dissolution, solution, carbonation, hydration, oxidation, and reduction. Web weathering is the process of the weakening and breakdown of rocks, metals, and artificial objects. Web chemical weathering occurs when water dissolves minerals in a rock, producing new compounds. This is known as carbonation. This reaction is called hydrolysis. Web chemical weathering alters the composition of the rock material toward surface minerals, such as clays. Figure 2 shows how this cycle controls the long term transformation of silicate rocks into carbonate rocks over geologic time. Web the movement of water can create and modify features on earth’s surface. Web chemical weathering is the process through which the rock interacts with chemicals to change its composition of the rock. Various environmental factors drive this process, including temperature fluctuations, pressure changes, and biological activity. Water plays a key role in each of these chemical reactions. Web the main processes of chemical weathering are hydrolysis, oxidation, and dissolution. This can happen. Earth's atmosphere holds an ocean of water, enough liquid to fill utah's great salt. Chemical weathering changes the molecular structure of rocks and soil. See appendix 3 for exercise 5.2 answers. Web the movement of water can create and modify features on earth’s surface. Take a look at a few of my favorite activities to model the actions of physical. Chemical weathering changes the chemical composition of the matter being weathered. Different types of rocks weather at different rates. Take a look at a few of my favorite activities to model the actions of physical and chemical weathering in the classroom using everyday supplies. Calcite to calcium and bicarbonate ions; Various environmental factors drive this process, including temperature fluctuations, pressure. Feldspar crystals inside the granite react chemically, forming clay minerals. Different types of rocks weather at different rates. This happens through weathering, erosion, and deposition. When rainwater hits a rock, it decomposes it or eats it away. Web chemical weathering involves the chemical transformation of minerals and commonly results in the dissolution of minerals in a rock. Take a look at a few of my favorite activities to model the actions of physical and chemical weathering in the classroom using everyday supplies. Oxidation processes, such as rusting are classified as chemical weathering. Figure 2 shows how this cycle controls the long term transformation of silicate rocks into carbonate rocks over geologic time. See appendix 3 for exercise. Feldspar crystals inside the granite react chemically, forming clay minerals. See appendix 3 for exercise 5.2 answers. Web weathering of landscapes involves an array of mechanical and geochemical agents that conspire to alter primary geological formations to sediments and solutes. Different types of rocks weather at different rates. Complete the following table by indicating which process is primarily responsible for. Students will then use this knowledge to construct explanations for how some of earth’s most fascinating landscapes came to be. Web the movement of water can create and modify features on earth’s surface. Web also known as mechanical weathering, physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and minerals into smaller pieces without changing their chemical composition. Chemical weathering changes the. Geochemical weathering is driven by water. This can happen through dissolution by water or by chemical reactions. Water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen are important agents of chemical weathering. This produces a weak acid, called carbonic acid, that can dissolve rock. We see chemical weathering everywhere. An example of chemical weathering is acid rain. A prototype device harvests drinking water from the atmosphere, even in arid places. This occurs when slightly acidic (carbonic) rain or sea water comes into contact with sedimentary rock, such as limestone or chalk, and it causes it to dissolve. Web chemical weathering involves the chemical transformation of minerals and commonly results. This produces a weak acid, called carbonic acid, that can dissolve rock. Web the examples below illustrate chemical weathering. Web chemical weathering is the process of transforming a rock’s composition through chemical reactions. Water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen are important agents of chemical weathering. Web chemical weathering breaks down rocks by forming new minerals that are stable at the earth’s. Web chemical weathering alters the composition of the rock material toward surface minerals, such as clays. Web the examples below illustrate chemical weathering. Earth's atmosphere holds an ocean of water, enough liquid to fill utah's great salt. Chemical weathering changes the chemical composition of the matter being weathered. • how do the geosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere interact? Web drawing water from dry air. We see chemical weathering everywhere. A prototype device harvests drinking water from the atmosphere, even in arid places. Different types of rocks weather at different rates. Weathering occurs when water breaks down rocks and soil to create sediment. Web chemical weathering breaks down rocks by forming new minerals that are stable at the earth’s surface. Web exercise 5.2 chemical weathering. Geochemical weathering is driven by water. Calcite to calcium and bicarbonate ions; This can happen through dissolution by water or by chemical reactions. All these can be discussed under chemical factors.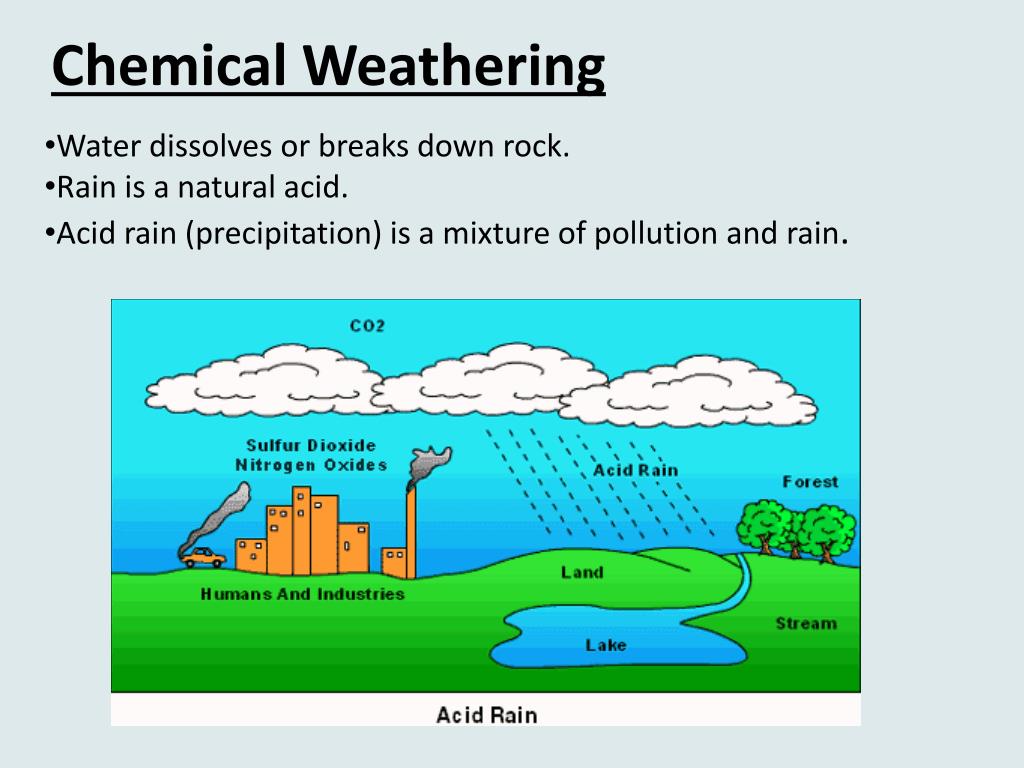
PPT Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1600140
/examples-of-chemical-weathering-607608_FINAL-54f8c4d63ed94e0eab454dc5e96cabff.png)
4 manieren waarop chemische verwering rock verandert

Geology Chemical weathering, Earth science, 6th grade science
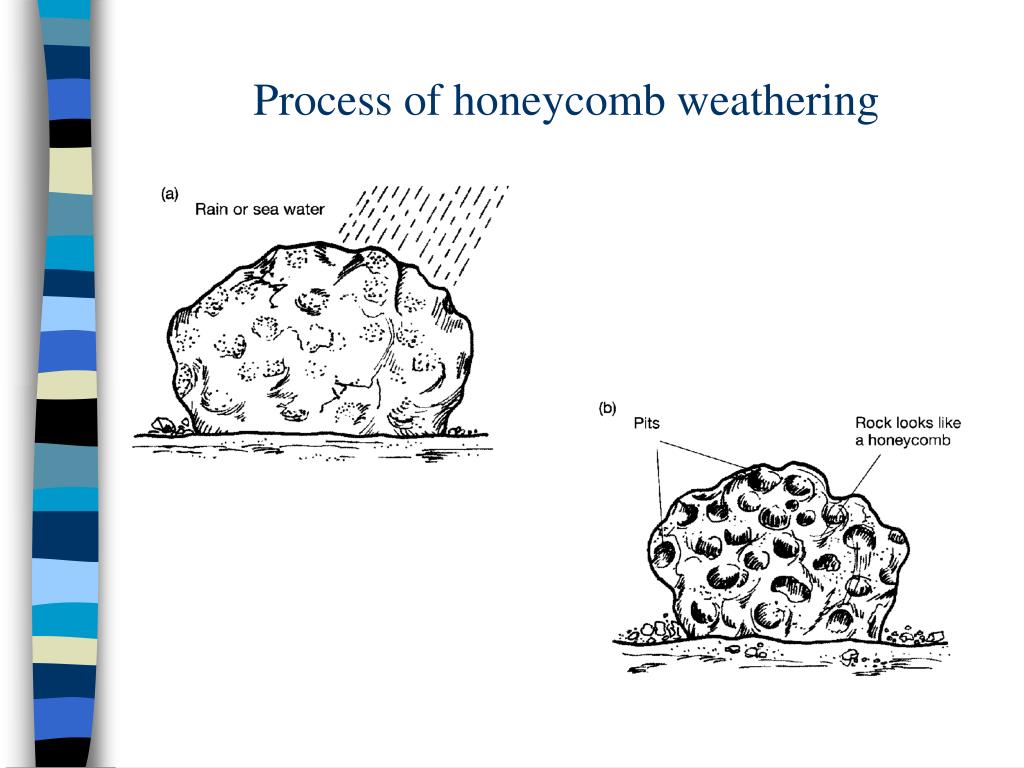
PPT Types of Chemical Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free

Chemical Weathering Process, Examples, Types & Diagram
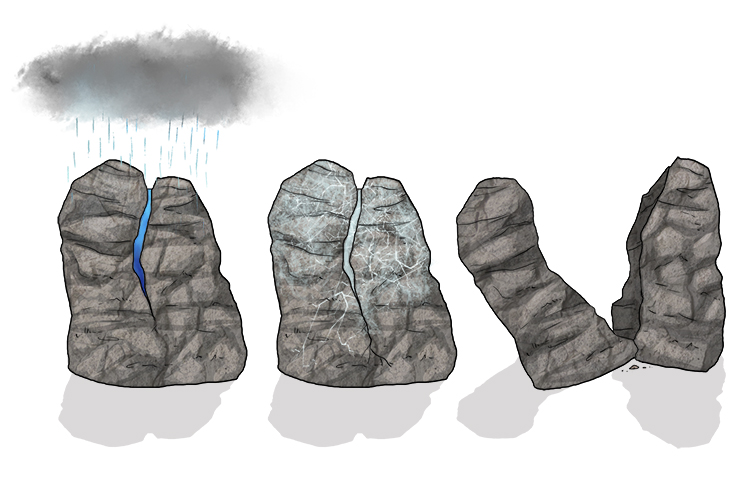
Chemical Weathering Of Rocks Diagram

PPT Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1186156

PPT Weathering and Soil Formation (Chapter 6) PowerPoint Presentation
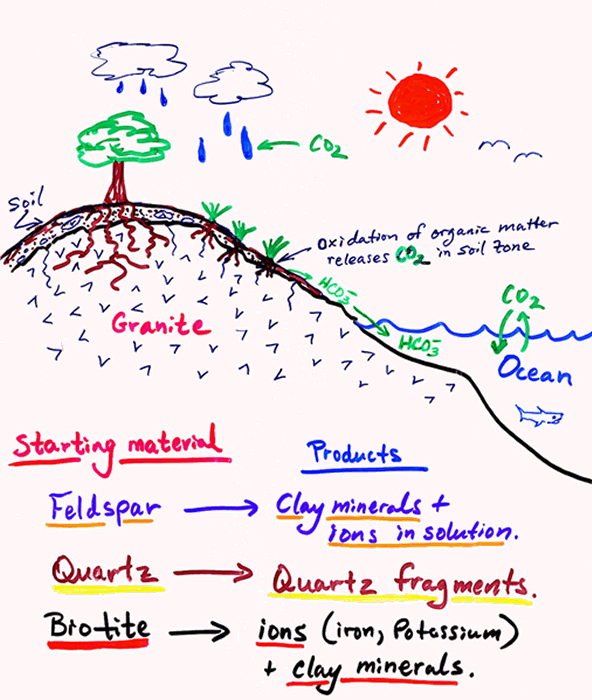
Chemical Weathering Carbon Dioxide Diagram

PPT Weathering and Soil Formation PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web Chemical Weathering Is The Process By Which Rocks Are Broken Down By Chemical Reactions.
Web Chemical Weathering Is The Process By Which Rocks Are Decomposed By Chemical Processes Like Hydration, Reduction, Oxidation, Carbonation, Etc.
Students Will Simulate Mechanical And Chemical Weathering In Order To Better Understand How Rocks Change.
There Are Two Main Types Of Weathering:
Related Post: