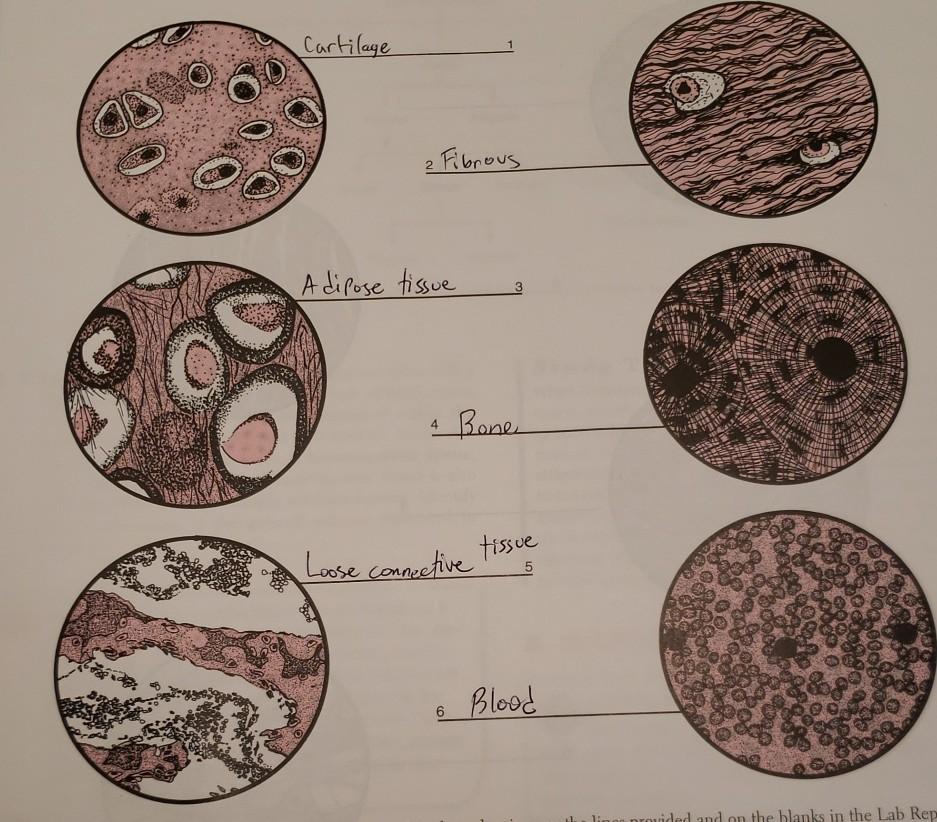
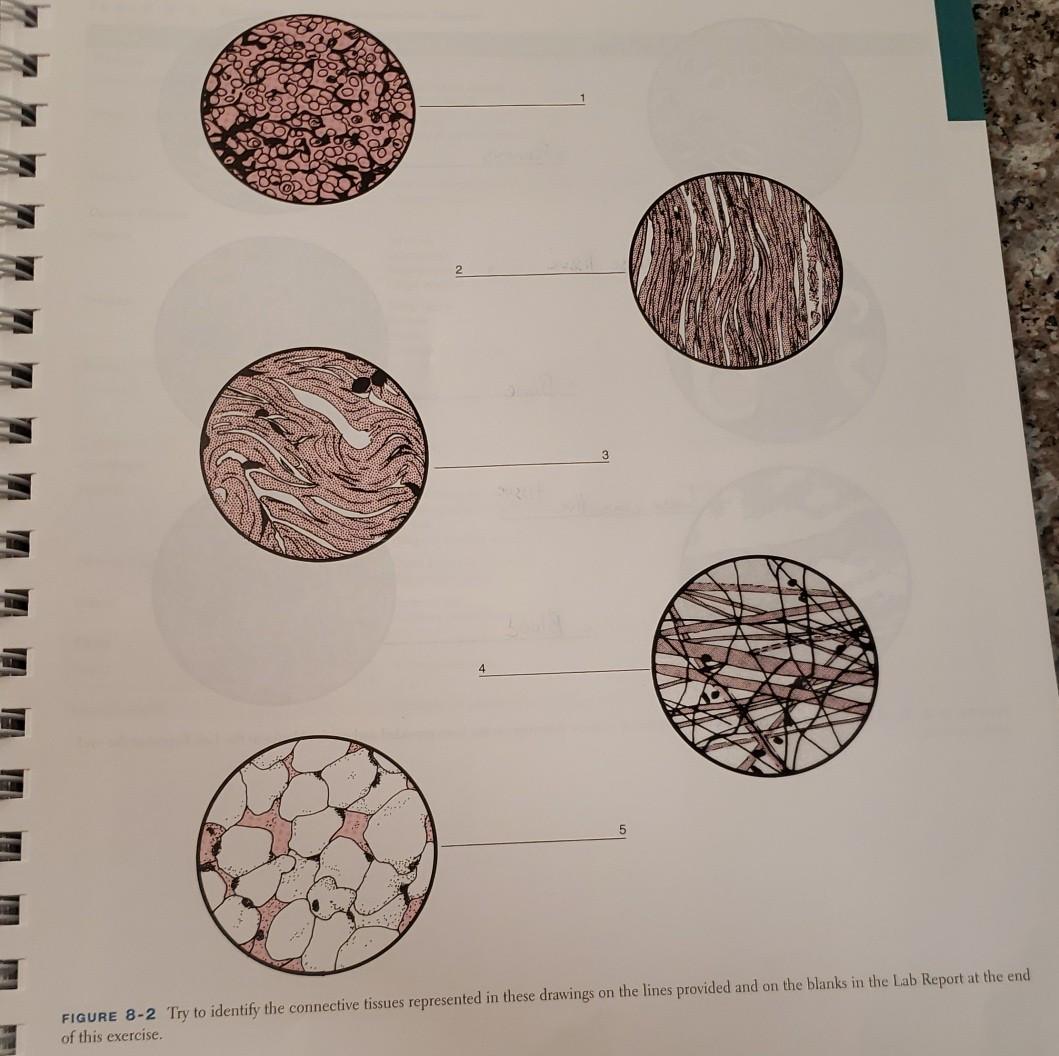
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing, Web reticular connective tissue forms an internal scaffolding for certain organs, such as lymph nodes, bone marrow, and the spleen.
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing - Web recognize different types of connective tissue (e.g., dense irregular, dense regular, loose, adipose) and know examples where they are found in the body. Web reticular connective tissue forms a structural framework for many tissues and organs, including bone marrow and lymphoid organs. These serve to hold organs and other tissues in place and, in the case of adipose tissue, isolate and store energy reserves. O is building an entire video library that will allow anyone to learn microbiology and anatomy & physiology for free. Feel free to reach out if there ar. If there is little space between protein fibers, the tissue is likely one of the dense connective tissues. Together the fibers and ground substance make up the extracellular matrix. Web reticular connective tissue 10x. Web reticular tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with an extracellular matrix consisting of an interwoven network of reticular fibers that provide a strong yet somewhat flexible framework (known as the stroma) for other types of functional cells to anchor within an organ or tissue. Web reticular fibers are abundant in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen), bone marrow and liver. Web loose connective tissue proper includes adipose tissue, areolar tissue, and reticular tissue. Its subunits, the reticular fibers, are predominant structures in the human body, but they are mainly scattered and mixed with other types of fibers. These serve to hold organs and other tissues in place and, in the case of adipose tissue, isolate and store energy reserves. Web. This page is maintained by the university of massachusetts biology department. Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this tissue type are they dominant. Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. This scaffolding supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages.. Recognize basement membranes (or basal lamina) in light micrograph and em sections and know their functions. Web reticular connective tissue is composed of a meshwork of reticular fibers (type iii collagen) in an open arrangement. Web reticular connective tissue forms a structural framework for many tissues and organs, including bone marrow and lymphoid organs. Web reticular connective tissue forms an. Web o compare the molecular makeup, structural organization, location, and functions of the three main fiber types of connective tissue. The textbook tends to have perfect quality images of specimens at high magnifications, instead try looking at your classmates’ more realistic images when studying for a practical. O is building an entire video library that will allow anyone to learn. The textbook tends to have perfect quality images of specimens at high magnifications, instead try looking at your classmates’ more realistic images when studying for a practical. This scaffolding supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages. A slide of reticular connective tissue from a human spleen. *font labels changed to red for easier visualization because. Reticular fibers are composed of thin and delicately woven strands of type iii collagen. Web loose connective tissue proper includes adipose tissue, areolar tissue, and reticular tissue. This scaffolding supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages. Web reticular connective tissue forms a structural framework for many tissues and organs, including bone marrow and lymphoid organs.. Web reticular tissue is a specific form of connective tissue predominating in several regions with high cellular content. *font labels changed to red for easier visualization because the slide was stained dark. Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. Web reticular connective tissue 20x. Reticular tissue, a type of loose. They are not visible with hematoxylin & eosin (h&e), but. Web o compare the molecular makeup, structural organization, location, and functions of the three main fiber types of connective tissue. Web reticular connective tissue is composed of a meshwork of reticular fibers (type iii collagen) in an open arrangement. Reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular. A slide of reticular connective tissue from a human spleen. Together the fibers and ground substance make up the extracellular matrix. These serve to hold organs and other tissues in place and, in the case of adipose tissue, isolate and store energy reserves. If there is little space between protein fibers, the tissue is likely one of the dense connective. Web reticular tissue is a specific form of connective tissue predominating in several regions with high cellular content. Web o compare the molecular makeup, structural organization, location, and functions of the three main fiber types of connective tissue. This page is maintained by the university of massachusetts biology department. Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only. This special connective tissue forms the stroma for hemopoietic tissues and lymphoid structures and organs, except the thymus. *font labels changed to red for easier visualization because the slide was stained dark. Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this tissue type are they dominant. They are not visible with hematoxylin & eosin (h&e), but. This scaffolding supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages. If there is abundant space between protein fibers, the tissue is likely one of the loose connective tissues. Web loose connective tissue proper includes adipose tissue, areolar tissue, and reticular tissue. Reticular fibers are composed of thin and delicately woven strands of type iii collagen. This page is maintained by the university of massachusetts biology department. Its subunits, the reticular fibers, are predominant structures in the human body, but they are mainly scattered and mixed with other types of fibers. The textbook tends to have perfect quality images of specimens at high magnifications, instead try looking at your classmates’ more realistic images when studying for a practical. Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. Connective tissue consists of three main components: O correlate the histological compositions and organizations of ct proper, reticular ct, and adipose ct and their locations and functions Web reticular tissue is a specific form of connective tissue predominating in several regions with high cellular content. These serve to hold organs and other tissues in place and, in the case of adipose tissue, isolate and store energy reserves.Reticular Connective Tissue 20x Histology
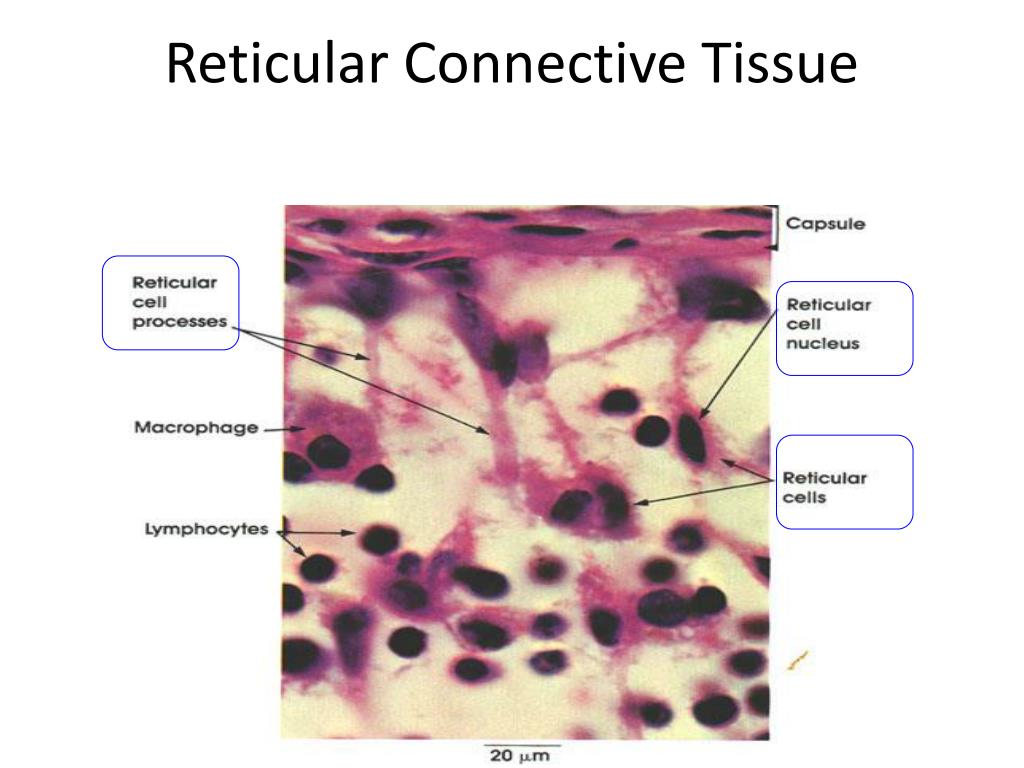
Reticular Connective Tissue Labeled

Reticular Connective Tissue Labeled
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing Master the Art of Illustrating
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing Master the Art of Illustrating

Reticular Connective Tissue Labeled

Reticular Connective Tissue, 40X Histology

Diagram of Reticular Connective Tissue Quizlet

Physiology Connective Tissues Histology ditki medical & biological
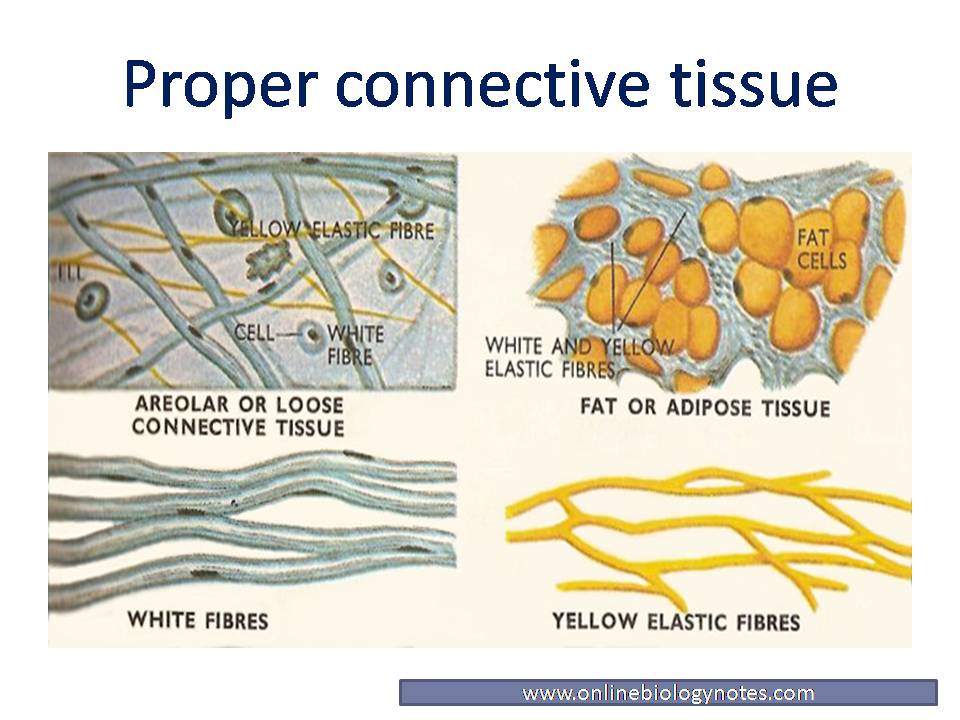
Loose Connective Tissue Reticular
Unlike Most Tissues, The Cells In Connective Tissue Are Not Necessarily Directly Bound Together And Instead Can Be Some Distance Apart Separated By Extracellular Matrix.
O Is Building An Entire Video Library That Will Allow Anyone To Learn Microbiology And Anatomy & Physiology For Free.
These Soft Organs Need An Internal Scaffolding Called The Stroma To.
Web Reticular Connective Tissue, 40X.
Related Post: