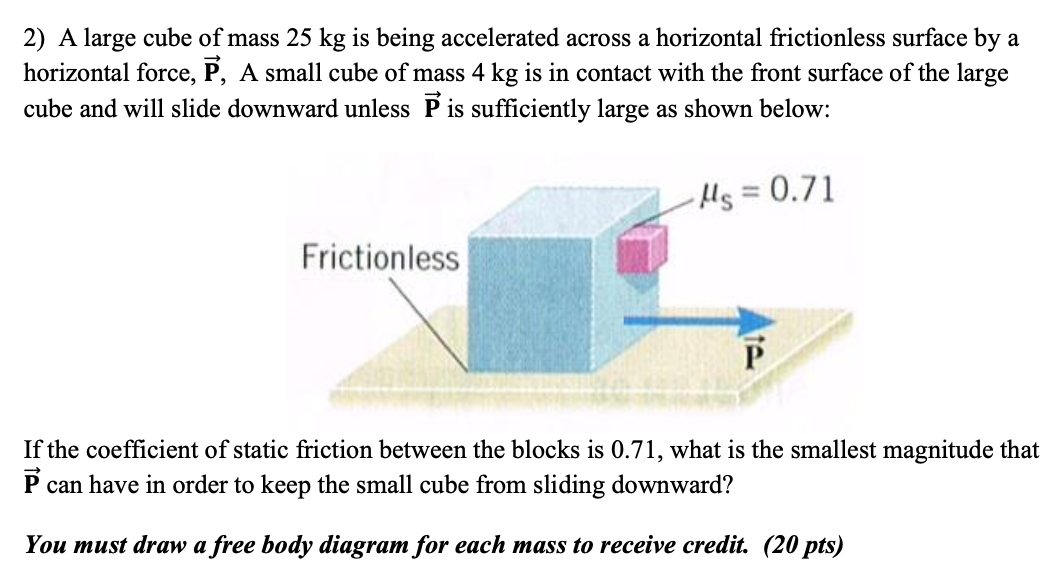
The Drawing Shows A Large Cube Being Accelerated, A small cube (mass = 2.1 kg) is in contact with.
The Drawing Shows A Large Cube Being Accelerated - A small cube mass is 4.0 kg is in contact with. There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. Web the drawing shows a large cube mass is 25kg, being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. The action off the weight. A small cube (mass = 4.1 kg) is in. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.9 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 2.1 kg) is in contact with. A small cube (mass =. There is one big cube and one small cube in this question. A small cube (mass = 4.4 kg) is. A small cube (mass =. A small cube (mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p is. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass 22.9 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated. A small cube (mass = 4.1 kg) is in. Since p is the only horizontal force acting on the system, it can be defined as the product of the acceleration by the total mass of. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{~kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\vec{p}$. A small. A small cube (mass = 2.1 kg) is in contact with. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. A small cube (mass = 4.4 kg) is. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass =. The big cube tends to move the right when a force p is exerted on it. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p.. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.9 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{~kg}$ ) being accelerated across. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 28.6 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with. A small cube(mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass $=25 \mathrm{kg}$ ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force $\mathbf{p}$. The coefficient of static friction between. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.0 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 4.1 kg) is. A small cube (mass = 4.5 kg) is. The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg ) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p →. A small cube(mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with. A small cube (mass 4.1 kg) is in contact with. The big cube tends to move the right when there. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact. Since p is the only horizontal force acting on the system, it can be defined as the product of the acceleration by the total mass of. A small cube (mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p is. Web. A small cube (mass = 2.1 kg) is in contact with. There is one big cube and one smaller cube. A small cube (mass = 3.6 kg) is in contact. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 48 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass 22.9 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. Web a small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p → is sufficiently large. Web the drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass=4.0 kg) is in contact with the front surface of the large cube and will slide downward unless p is. The action off the weight force is suffered. The coefficient of static friction between. The big cube tends to move the right when there is a force p on it. Web the drawing shows a large cube(mass=25 kg) being accelerated accross a frictionless surface by a horizontal force p. A small cube (mass = 4.0 kg) is in contact. The action off the weight. A small cube (mass = 4.4 kg) is.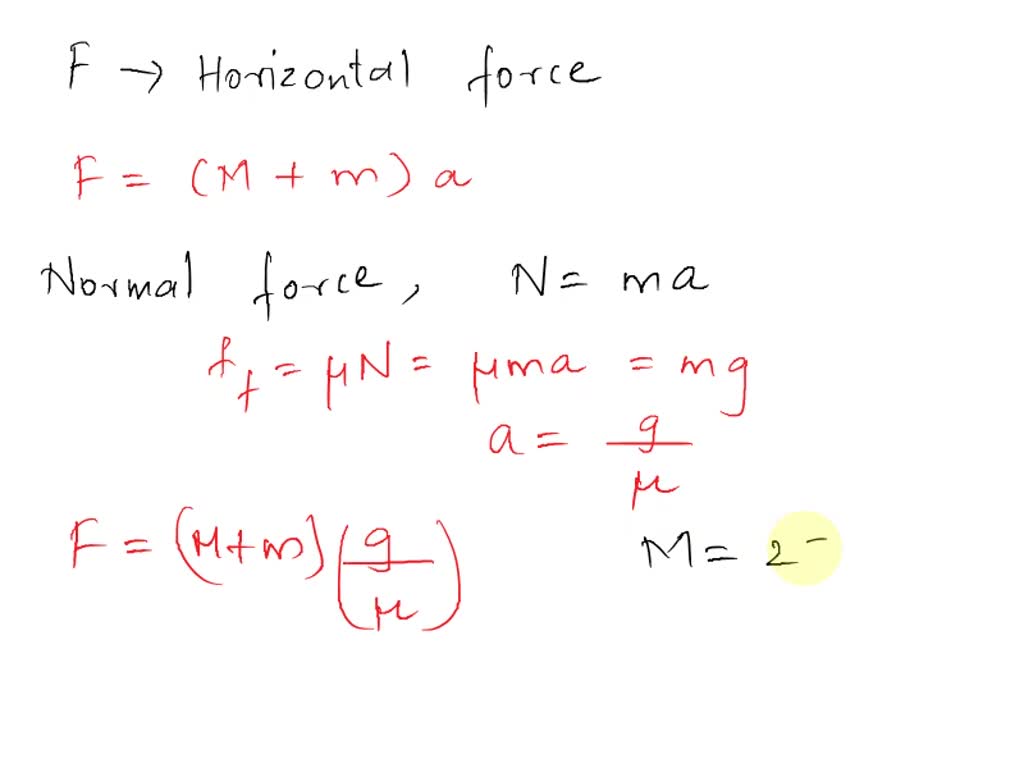
SOLVED The figure below shows large cube (mass 30kg) being accelerated

SOLVEDThe drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated

Answered *44. The drawing shows a large cube… bartleby
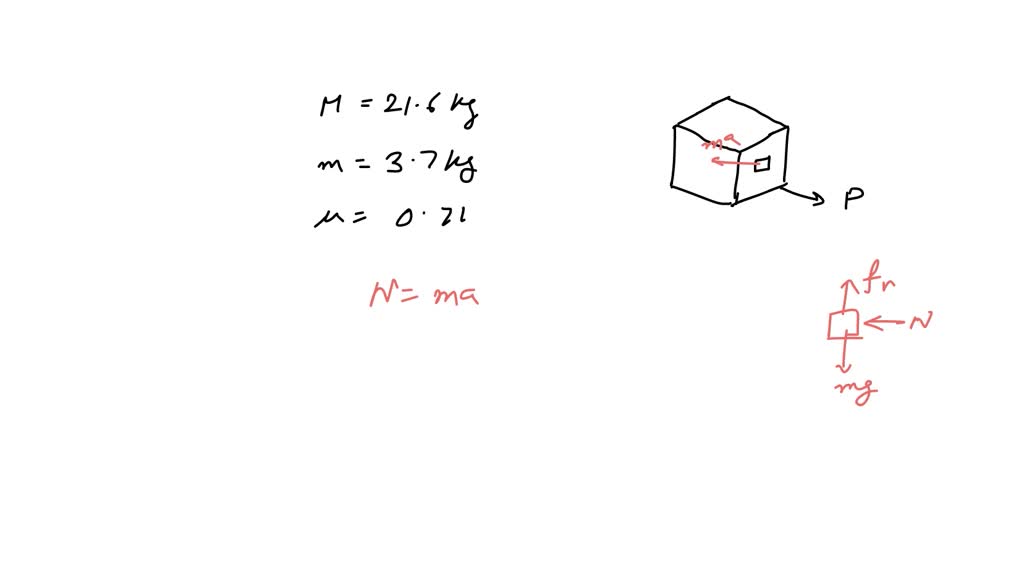
SOLVED The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 21.6 kg) being

SOLVEDThe drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated
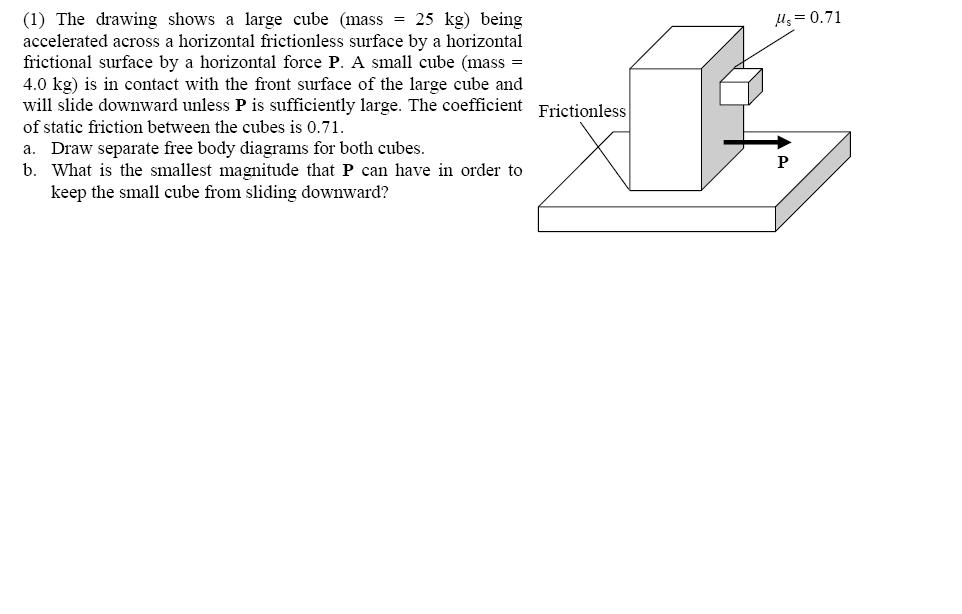
The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being

Solved 2) A large cube of mass 25 kg is being accelerated
Solved 2) A large cube of mass 25 kg is being accelerated

SOLVED The drawing shows a large cube (mass = 25 kg) being accelerated
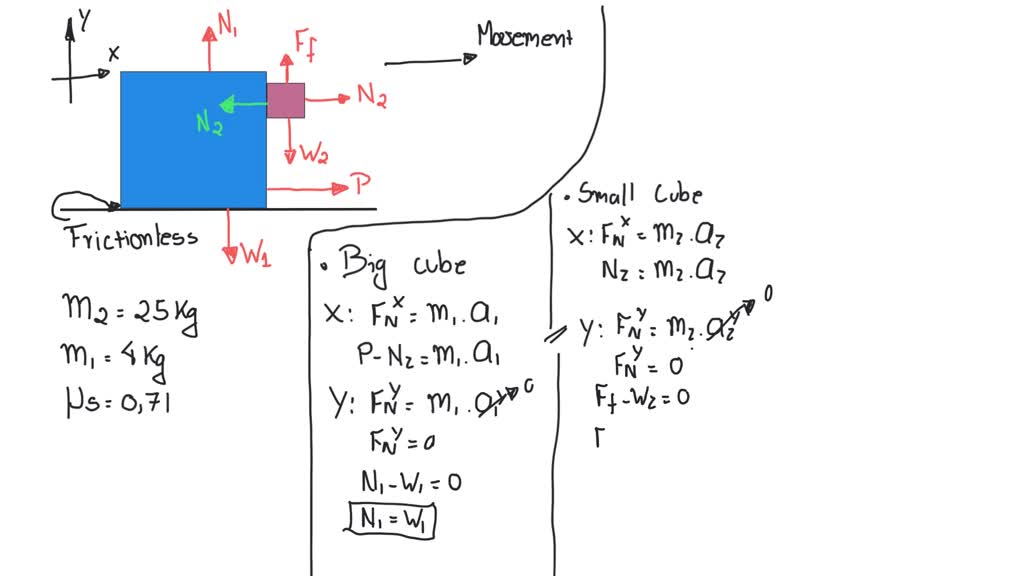
mmh The drawing shows a large cube (mass =25 kg ) being accelerated
Web The Drawing Shows A Large Cube (Mass = 25 Kg) Being Accelerated.
The Drawing Shows A Large Cube (Mass = 25 Kg ) Being Accelerated Across A Horizontal Frictionless Surface By A Horizontal Force P →.
A Small Cube (Mass = 4.5 Kg) Is.
A Small Cube (Mass = 4.1 Kg) Is In.
Related Post: