Ray Diagram Drawer, Web the goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the convex mirror.
Ray Diagram Drawer - Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. Web in a ray diagram, the initial point represents the source of light, while the ending point represents the observer's position. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: Each ray represents a beam of light, and they are. A ray of light is incident on a convex lens parallel to the principal axis, as shown below. Web how to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens. Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. Web image formation in lenses using ray diagrams. Web the goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the convex mirror. Web how to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens. Typically, this requires determining where the image. Identify and mark the object distance. Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. Web in a ray diagram, the initial point represents the source of light, while the ending point represents the. Web convex mirror has two ray diagrams because its principal focus and the centre of curvature lies behind its reflecting surface. Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Web the goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by. Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Identify the focal length of the concave lens ( f) and the distance from the center of the lens ( d ). Web image formation in lenses using ray diagrams. Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. Web convex mirror has. Draw the mirror and the object. Web the ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Identify the focal length of the concave lens ( f) and the distance from the center of the lens ( d ). It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging. Typically, this requires determining where. Identify and mark the object distance. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: This guide includes everything you need to know, from the basics of light rays to the more. Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. Identify the focal length of the concave lens ( f) and the distance from the center of the lens ( d ). This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. Draw the mirror and the object. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: Typically, this requires determining where the image. Web how to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens. Web this video covers: It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging. Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. This guide includes everything you need to know, from the basics of light rays to the more. Web the goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the convex mirror. Identify and mark the object distance. Web in a ray diagram, the initial point represents the source of. Typically, this requires determining where the image. This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. Web the goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the convex mirror. Web the ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar. Identify the focal length of the concave lens ( f) and the distance from the center of the lens ( d ). Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Web in a ray diagram, the initial point represents the source of light, while the ending point represents the observer's position.. Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. Identify the focal length of the concave lens ( f) and the distance from the center of the lens ( d ). Each ray represents a beam of light, and they are. Identify and mark the object distance. Web a ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: Web how to draw a ray diagram for a concave lens. Web convex mirror has two ray diagrams because its principal focus and the centre of curvature lies behind its reflecting surface. Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. It explains how to draw ray diagrams for converging. This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. Draw the mirror and the object. With an arrowhead pointing in the direction that the light travels. Typically, this requires determining where the image. Web in a ray diagram, the initial point represents the source of light, while the ending point represents the observer's position. Web this video covers:
How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo

Ray Diagram Drawer

Ray Diagram Drawer

How To Draw Ray Diagrams of all time Don t miss out howtodrawimages1
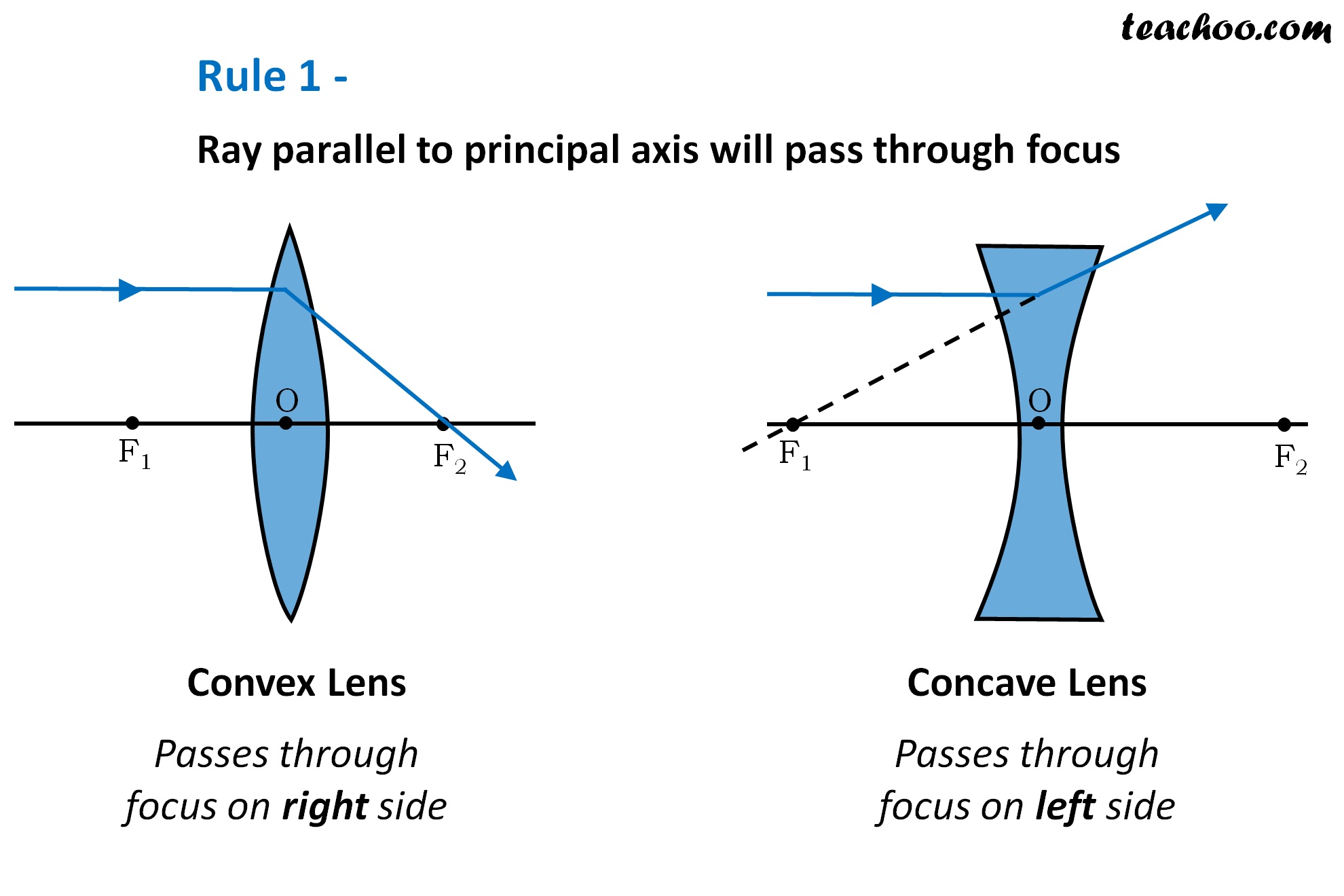
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
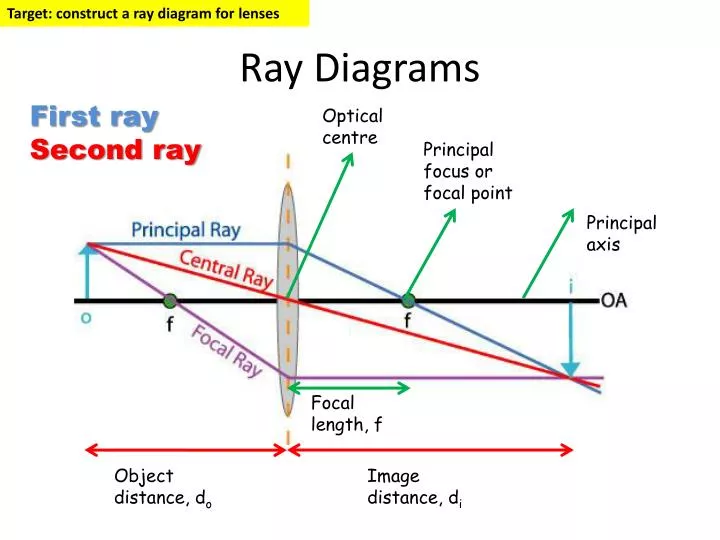
PPT Ray Diagrams PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6878954
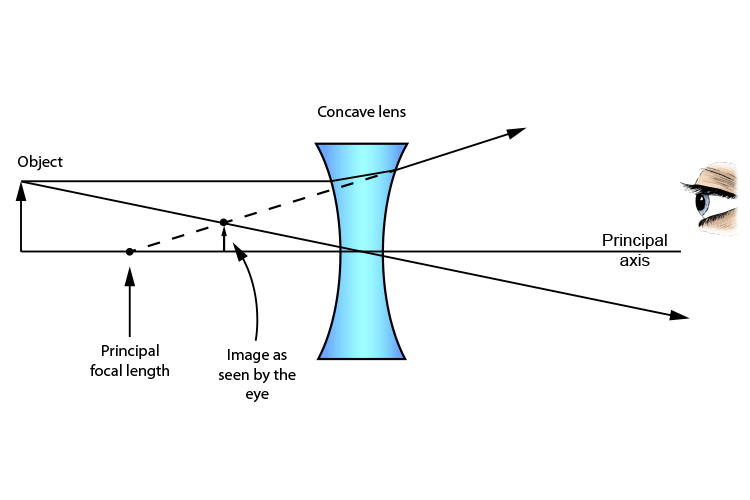
Ray Diagram Drawer
How to Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT)

How To Draw Ray Diagrams For Convex Mirrors vrogue.co
A Ray Of Light Is Incident On A Convex Lens Parallel To The Principal Axis, As Shown Below.
This Guide Includes Everything You Need To Know, From The Basics Of Light Rays To The More.
Web The Goal Of A Ray Diagram Is To Determine The Location, Size, Orientation, And Type Of Image That Is Formed By The Convex Mirror.
Web The Ray Nature Of Light Is Used To Explain How Light Refracts At Planar And Curved Surfaces;
Related Post:
