Neuron Drawing Labeled, Discover the different structural types of neurons:
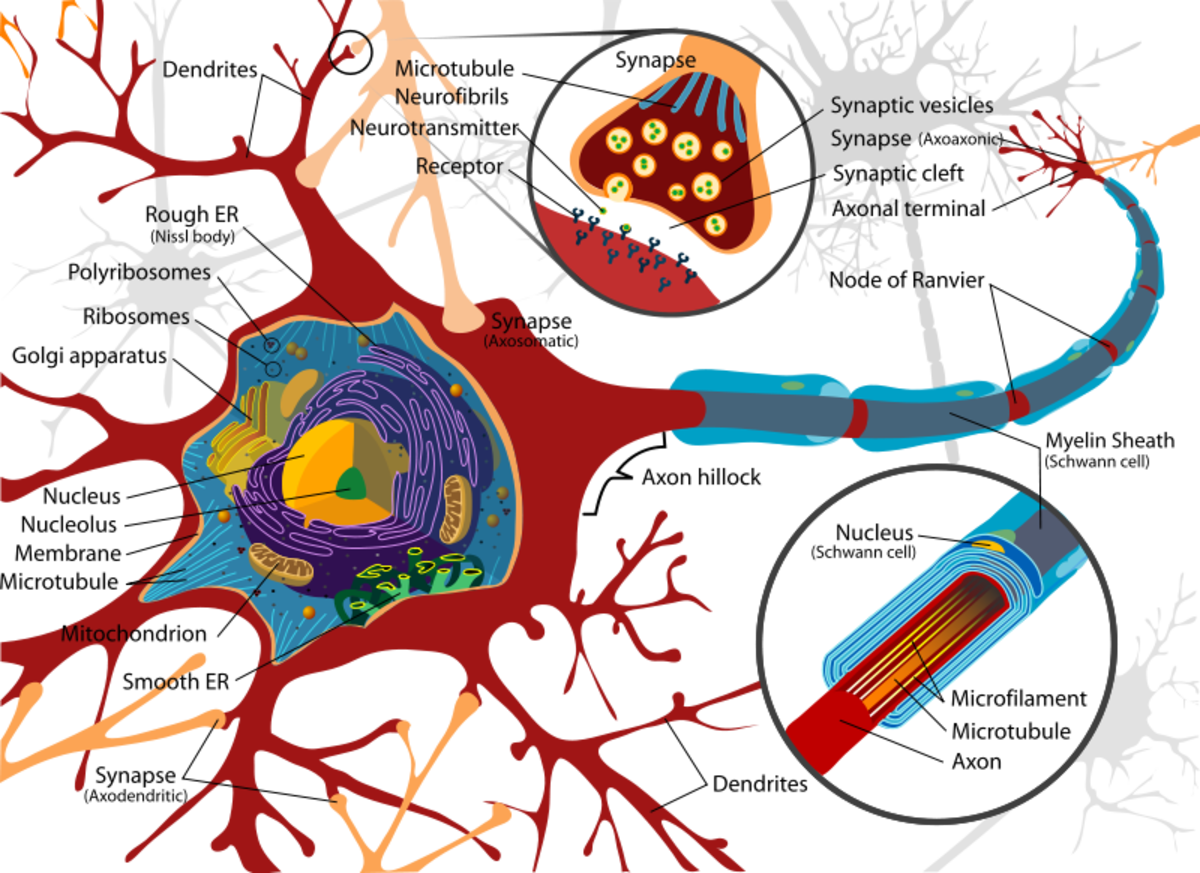
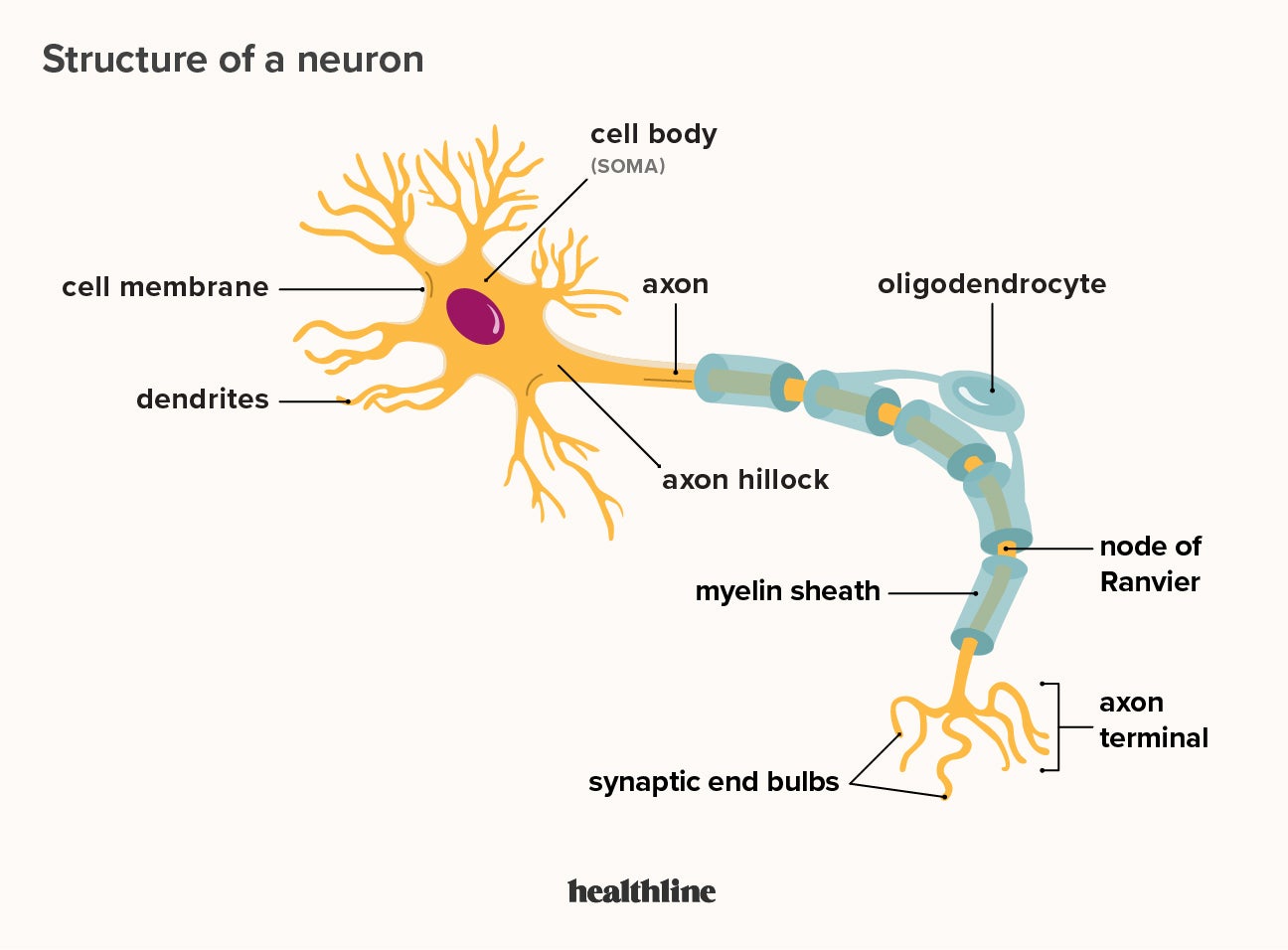
Neuron Drawing Labeled - Somatic motor neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of. Web to properly understand the coordination between the brain and the body, the students must learn about the neurons. Motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. (6) this neuron part receives messages from other neurons. Learn about the axon hillock, axon terminals, and the myelin sheath. Scn2a loss of function has the strongest association with asd of any known genetic mutation. A group of neurons forms a nerve. Web a neuron, neurone, [1] or nerve cell is an excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network in the nervous system. Signals are received through the dendrites, travel to the cell body, and continue down the axon until they reach the synapse (the communication point between two. Nerve cells are also some of the longest cells in your body. Uncover the roles of dendrites, axons, and the soma. They release neurotransmitters to trigger responses leading to. Web a diagram of a neuron also known as the nerve cell is useful as a visual tool to illustrate the various components of the neuron. Neurons are unique for many reasons. For one, they have a shape that is not like any. 1) dendrites , 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. Web the main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. It also helps us to understand the functions of the neuron. Neurons, also known as nerve cells, send and receive signals from your brain. Uncover the roles of dendrites, axons, and the soma. The neuron (or nerve cell) is the functional unit of both the central nervous system (cns) and the peripheral nervous system (pns). Neurons are composed of three main parts: Dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. Scn2a loss of function has the strongest association with asd of any known genetic mutation. Web a neuron is a nerve cell that processes. Web the following labeled diagram shows the parts of a neuron. Somatic motor neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of. Web to properly understand the coordination between the brain and the body, the students must learn about the neurons. Neurons are composed of three main parts: Neurons form the bulk. 1) dendrites , 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. (8) this neuron part gives messages to muscle tissue. Web all neurons have three main parts: Web motor neurons (also referred to as efferent neurons) are the nerve cells responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system towards muscles to cause movement. (9) this neuron part processes. Web a diagram of a neuron also known as the nerve cell is useful as a visual tool to illustrate the various components of the neuron. There are three main categories of neurons: Web drawing of the helmet used in the study. Scn2a loss of function has the strongest association with asd of any known genetic mutation. (7) this neuron. There are nerve cells as long as a meter. Web in the neuron drawing shown below, the neuron is labeled to show structures such as the cell body, axons, dendrites, and synapses. There are three main categories of neurons: Web diagram of neuron with labels. Neurons are composed of three main parts: Discover the different structural types of neurons: Web a diagram of a neuron also known as the nerve cell is useful as a visual tool to illustrate the various components of the neuron. 1) dendrites , 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. Web the main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. Web. Web explore the structure of neurons, their types, and functions. They release neurotransmitters to trigger responses leading to. A group of neurons forms a nerve. The researchers examined how the brain controls this reflex in people and mice with a genetic mutation called scn2a loss of function. (8) this neuron part gives messages to muscle tissue. Explore the complexities, differences and intricate details of our neurons. Motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. Unipolar, bipolar, multipolar, and pseudounipolar. (9) this neuron part processes incoming messages. (7) this neuron part sends on messages to other neurons. It also helps us to understand the functions of the neuron. Web how the structure of a neuron allows it to receive and transmit information. There are nerve cells as long as a meter. Web drawing of the helmet used in the study. Motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. Neurons are composed of three main parts: Neurons are unique for many reasons. In order to make it more understandable to the students, we have added all the functions of the neuron in the labeled diagram. Nerve cells are also some of the longest cells in your body. Web a diagram of a neuron also known as the nerve cell is useful as a visual tool to illustrate the various components of the neuron. A group of neurons forms a nerve. The neuron is a specialized and individual cell, which is also known as the nerve cell. Scn2a loss of function has the strongest association with asd of any known genetic mutation. Web in the neuron drawing shown below, the neuron is labeled to show structures such as the cell body, axons, dendrites, and synapses. Here is the description of human neuron along with the diagram of the neuron and their parts. Cell body of a nerve cell (perikaryon) the cell body of neuron is called soma or perikaryon.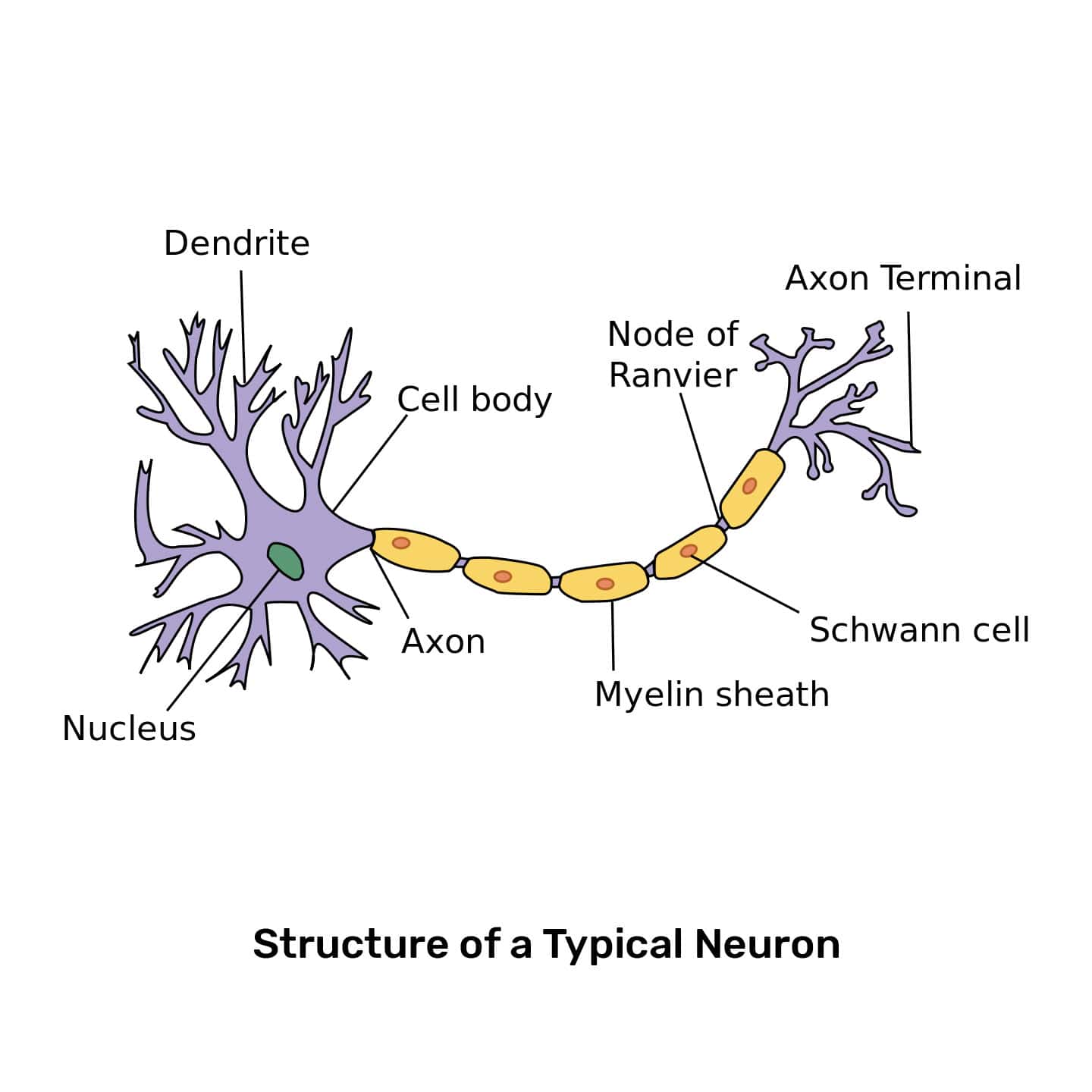
Kids Corner Gabrieli Lab
Structure of a Neuron Owlcation
What Is a Neuron? Diagrams, Types, Function, and More
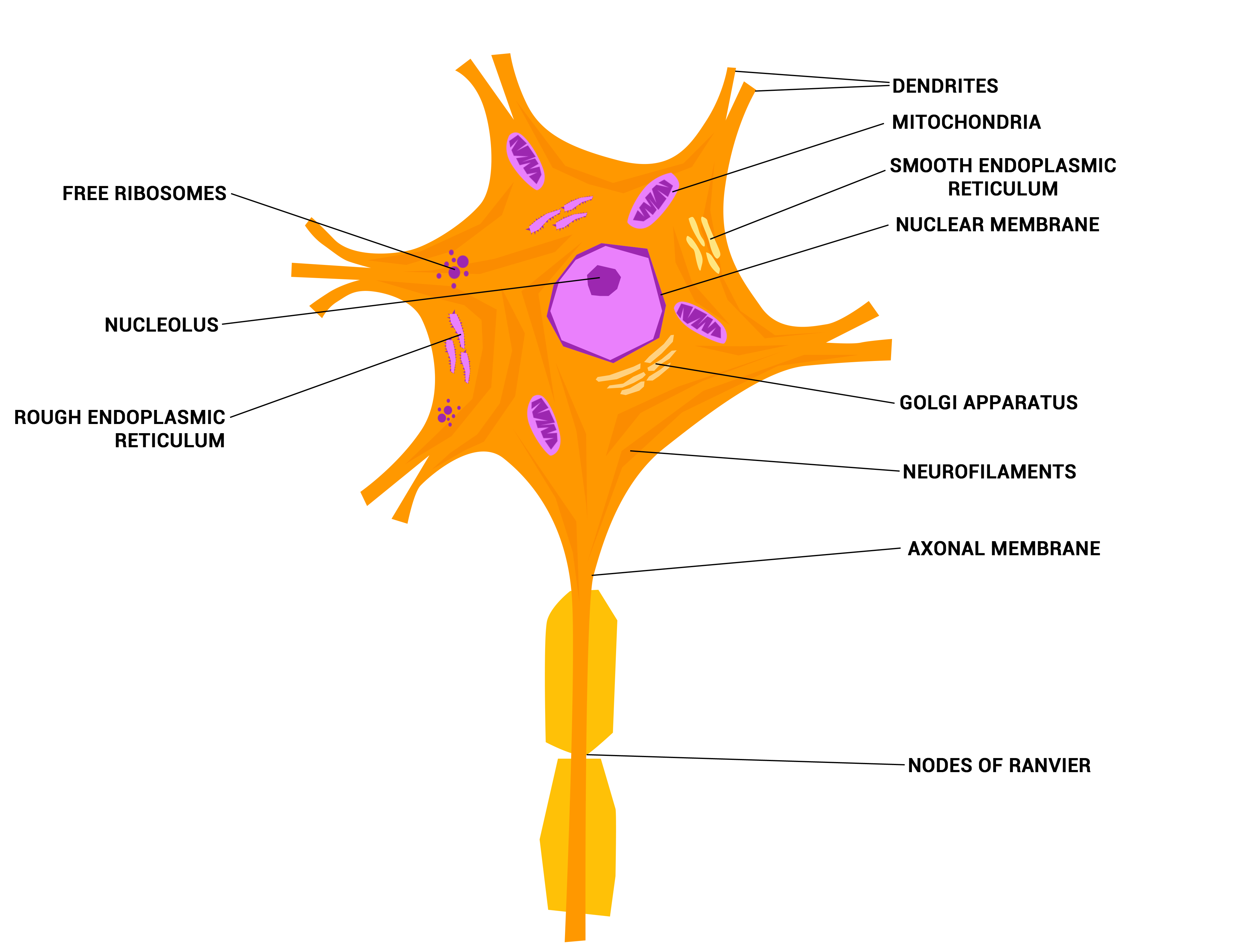
Diagram Of A Neuron Labeled
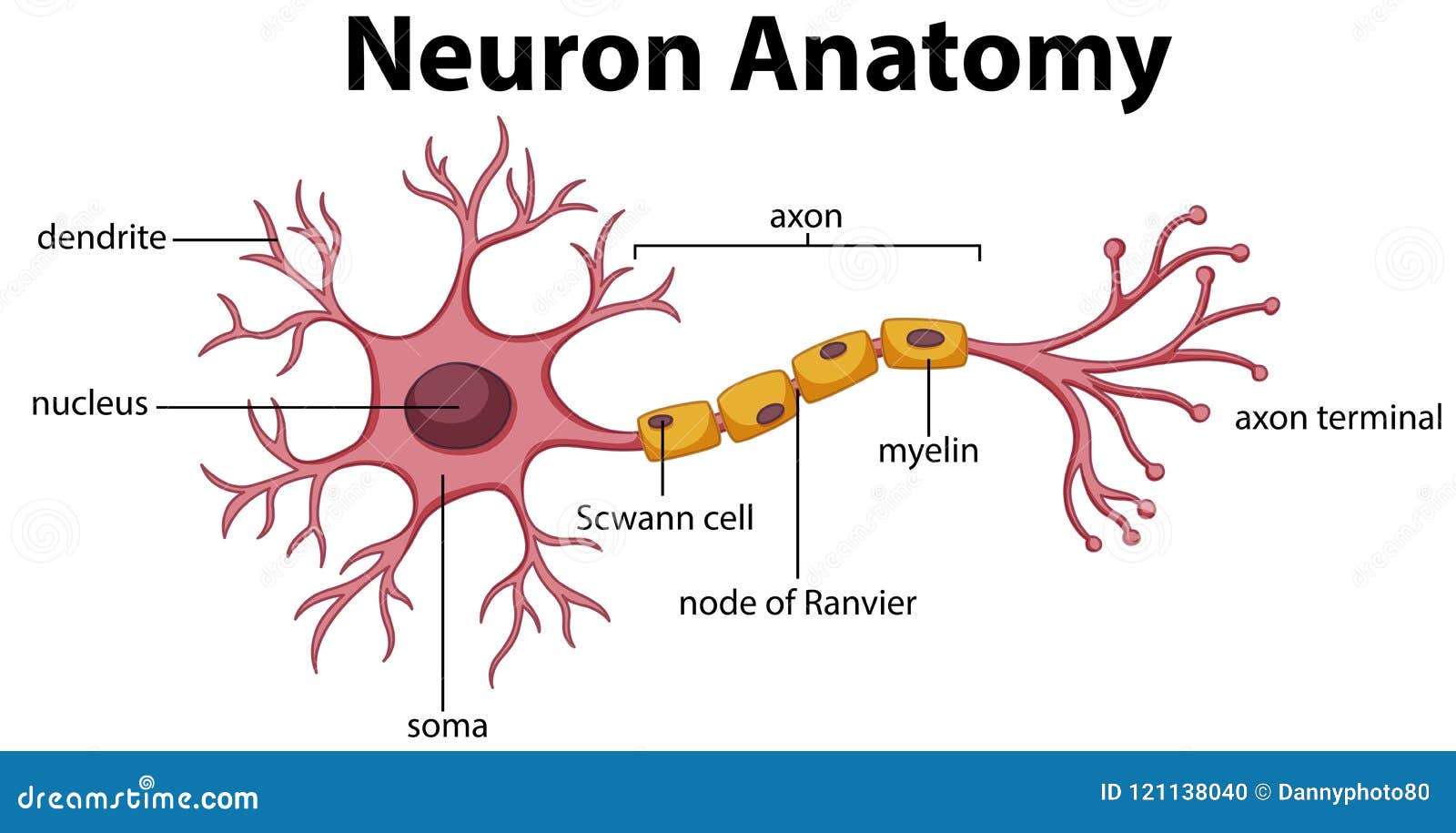
Diagram of Neuron Anatomy stock vector. Illustration of drawing 121138040
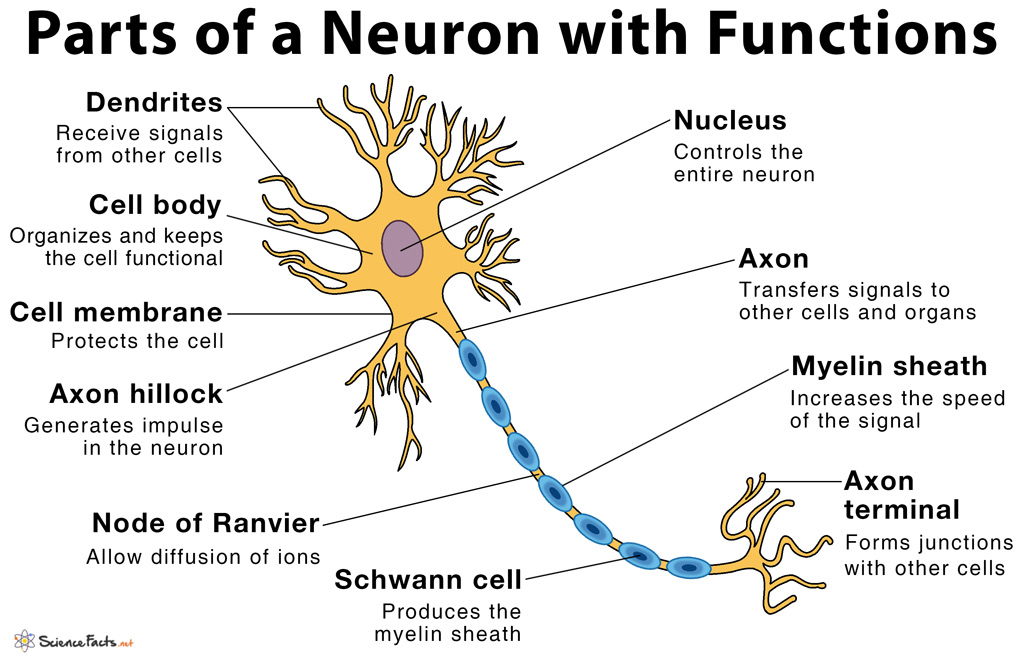
Parts of a Neuron and Their Functions with Labelled Diagram
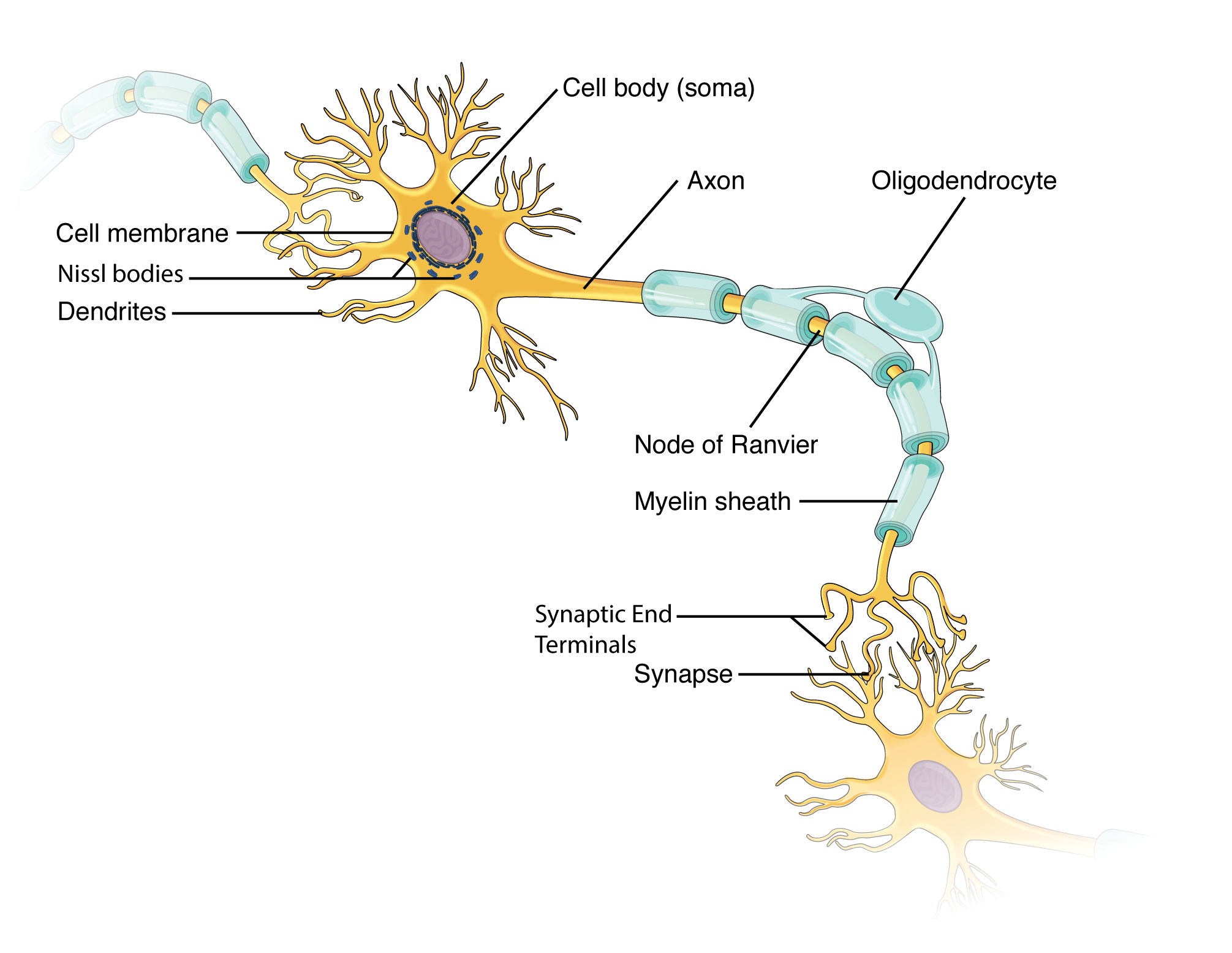
Neuron Labeled And Functions
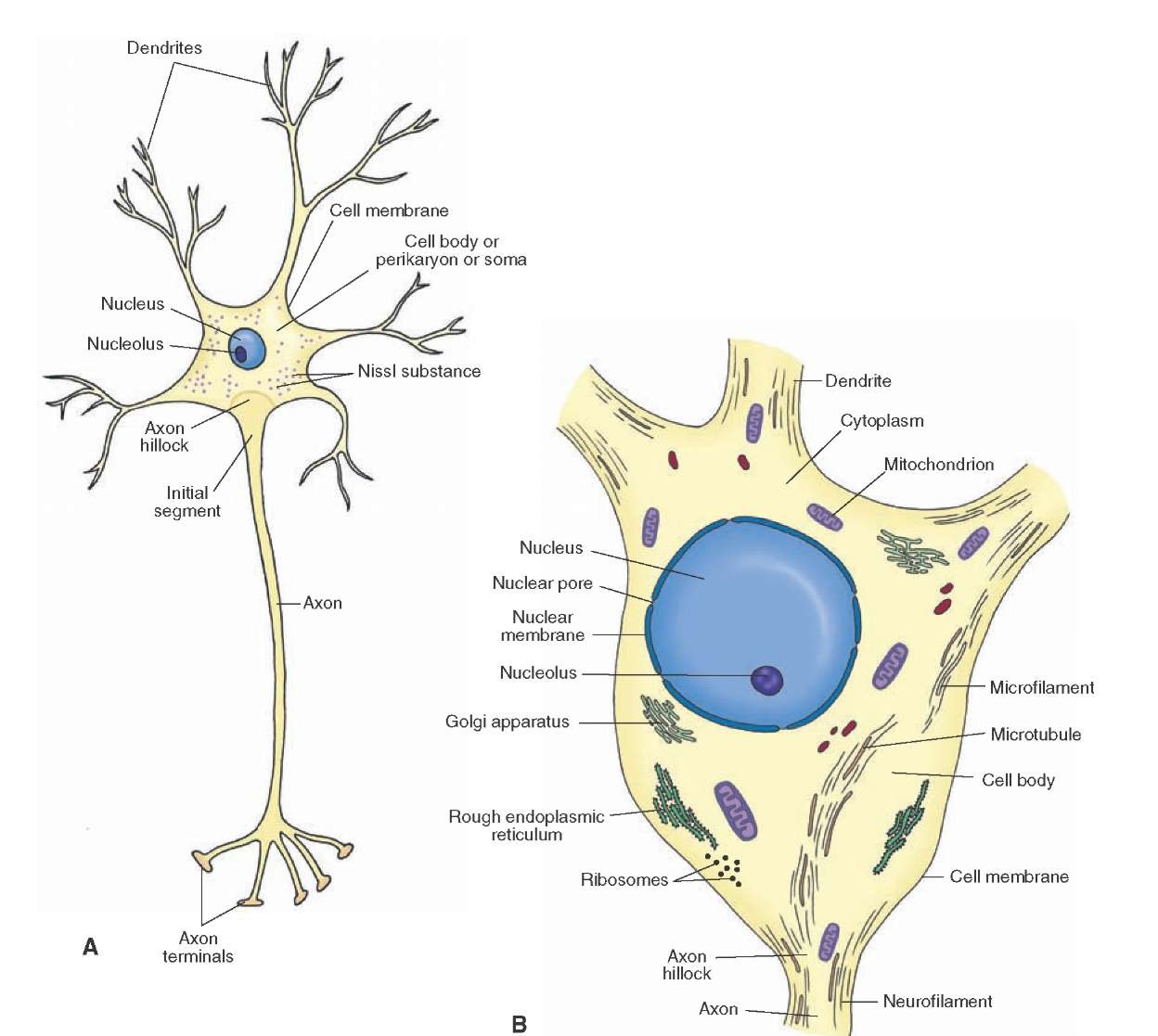
Histology of the Nervous System (The Neuron) Part 1

Explain The Structure Of Neuron With Diagram

NeuronDiagram Straight from a Scientist
The Researchers Examined How The Brain Controls This Reflex In People And Mice With A Genetic Mutation Called Scn2A Loss Of Function.
How Do You Know Where You Are Right Now?
Neurons Are Information Carrier Cells Within The Central Nervous System (Cns) And Peripheral Nervous System (Pns).
Uncover The Roles Of Dendrites, Axons, And The Soma.
Related Post: