Mutualism Drawing, Web competition, predation, and mutualism.
Mutualism Drawing - Web here it is essential to differentiate commensalism from mutualism, parasitism, and amensalism. Web mutualism in biology refers to symbiotic species interactions that are mutually beneficial, or even essential, for survival. Web mutualism is an association or symbiotic interaction between the organisms of two different species in which each is benefited. It is a symbiotic relationship in which two different species interact with and in some cases, totally rely on one another for survival. In a mutualism, both species benefit from their interaction. Other scientists think that symbiotic relationships apply to parasitic relationships as well as mutualistic ones. Imagine you are diving in the pacific ocean. For example, ants living in a tree may protect the tree from an organism that would like to make the tree its next meal, and at the same time the tree provides a safe home for the ants. Here, you might spot a group of clownfish swimming in a bed of sea anemones. Mutualistic arrangements are most likely to develop between organisms with widely different living requirements. Web a symbiosis is an evolved interaction or close living relationship between organisms from different species, usually with benefits to one or both of the individuals involved. Explore its types and examples only @ byju's. Web in biology, mutualism is defined as an ecological relationship between two or more species in which both members benefit. Web mutualism describes a type. For example, ants living in a tree may protect the tree from an organism that would like to make the tree its next meal, and at the same time the tree provides a safe home for the ants. The three relationships — mutualism commensalisms, and parasitism — are the type of organism that exhibits symbiosis. Imagine you are diving in. Web the concept of a mutualism is in contrast to interspecific competition, which occurs when organisms from different species compete for a resource, resulting in reduced fitness for one of the individuals or populations involved while the other benefits. An example of mutualism is a squirrel eating nuts or fruit from a tree, then dispersing the tree’s seeds in its. Web the concept of a mutualism is in contrast to interspecific competition, which occurs when organisms from different species compete for a resource, resulting in reduced fitness for one of the individuals or populations involved while the other benefits. For example, pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, benefit because they eat the collect pollen and/or nectar that they collect. Predatory interactions may reduce the number of organisms or eliminate whole populations of organisms. Web competition, predation, and mutualism. Mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and competition. Web here it is essential to differentiate commensalism from mutualism, parasitism, and amensalism. Other scientists think that symbiotic relationships apply to parasitic relationships as well as mutualistic ones. Web several studies have determined ecological or evolutionary conditions driving transitions from mutualism to antagonism (mutualism breakdown) (kiers et al. Web mutualism describes a type of mutually beneficial relationship between organisms of different species. The three relationships — mutualism commensalisms, and parasitism — are the type of organism that exhibits symbiosis. Web mutualistic interactions, or mutualisms, are ubiquitous in nature.. In a mutualism, both species benefit from their interaction. Web mutualistic interactions, or mutualisms, are ubiquitous in nature. Imagine you are diving in the pacific ocean. Web the concept of a mutualism is in contrast to interspecific competition, which occurs when organisms from different species compete for a resource, resulting in reduced fitness for one of the individuals or populations. The squirrel benefits because it receives food, and the tree benefits because its seeds are spread and can grow into more trees. Other scientists think that symbiotic relationships apply to parasitic relationships as well as mutualistic ones. It thus is a type of association where all the partners work together, with each partner benefiting from the relationship. Web a symbiosis. Mutually beneficial interactions, in contrast, may become so interdependent that each organism requires the other for survival. To learn about these relationships, let's imagine diving deep into the ocean. The squirrel benefits because it receives food, and the tree benefits because its seeds are spread and can grow into more trees. Web mutualism is a term used to describe a. Web mutualistic interactions, or mutualisms, are ubiquitous in nature. Web several studies have determined ecological or evolutionary conditions driving transitions from mutualism to antagonism (mutualism breakdown) (kiers et al. Here, you might spot a group of clownfish swimming in a bed of sea anemones. It is a symbiotic relationship in which two different species interact with and in some cases,. For example, ants living in a tree may protect the tree from an organism that would like to make the tree its next meal, and at the same time the tree provides a safe home for the ants. Mutually beneficial interactions, in contrast, may become so interdependent that each organism requires the other for survival. It thus is a type of association where all the partners work together, with each partner benefiting from the relationship. An example of mutualism is a squirrel eating nuts or fruit from a tree, then dispersing the tree’s seeds in its scat. It is a symbiotic relationship in which two different species interact with and in some cases, totally rely on one another for survival. In a mutualism, both species benefit from their interaction. Web a mutualism occurs when two species benefit from their interaction. Explore its types and examples only @ byju's. For example, pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, benefit because they eat the collect pollen and/or nectar that they collect from flowers. Imagine you are diving in the pacific ocean. Web focusing on a range of ecological and evolutionary aspects over different scales (from individual to ecosystem), the chapters in this book provide expert coverage of our current understanding of mutualism whilst highlighting the most important questions that. The squirrel benefits because it receives food, and the tree benefits because its seeds are spread and can grow into more trees. Web mutualisms have shaped evolution in many ways, for example, animal and plant cells arose from a mutualism between different bacteria, with one forming the main cells and the other forming organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. Web mutualistic interactions, or mutualisms, are ubiquitous in nature. Web mutualism in biology refers to symbiotic species interactions that are mutually beneficial, or even essential, for survival. Web mutualism describes a type of mutually beneficial relationship between organisms of different species.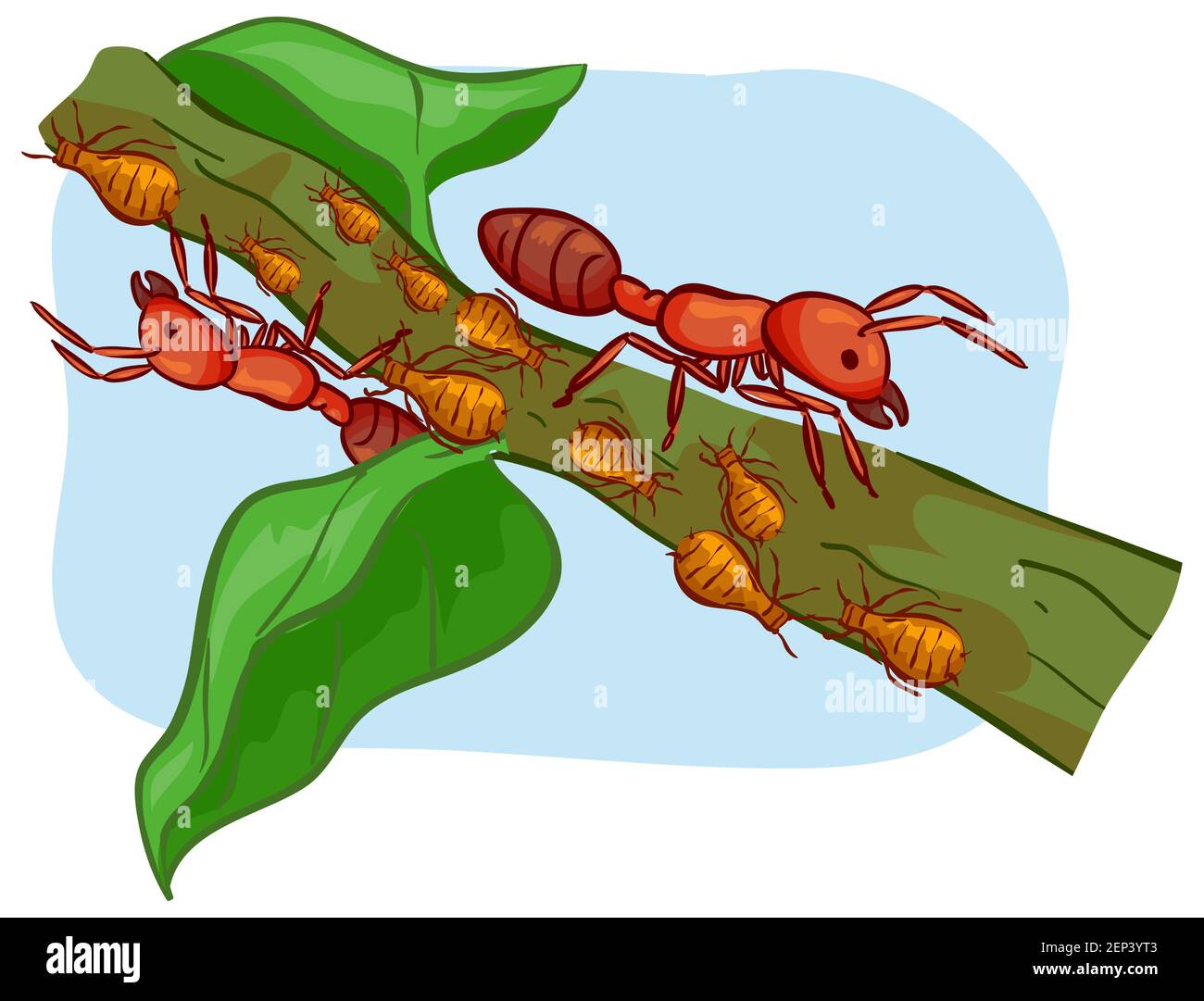
Illustration of Ants and Aphids Crawling on a Branch, Symbiotic

Mutualism Drawing by Nancy White during the May 6, 2010 Ga… Flickr

Learn to Draw Mutualism Ghost Pipes and Tube Worms Sierra Club BC
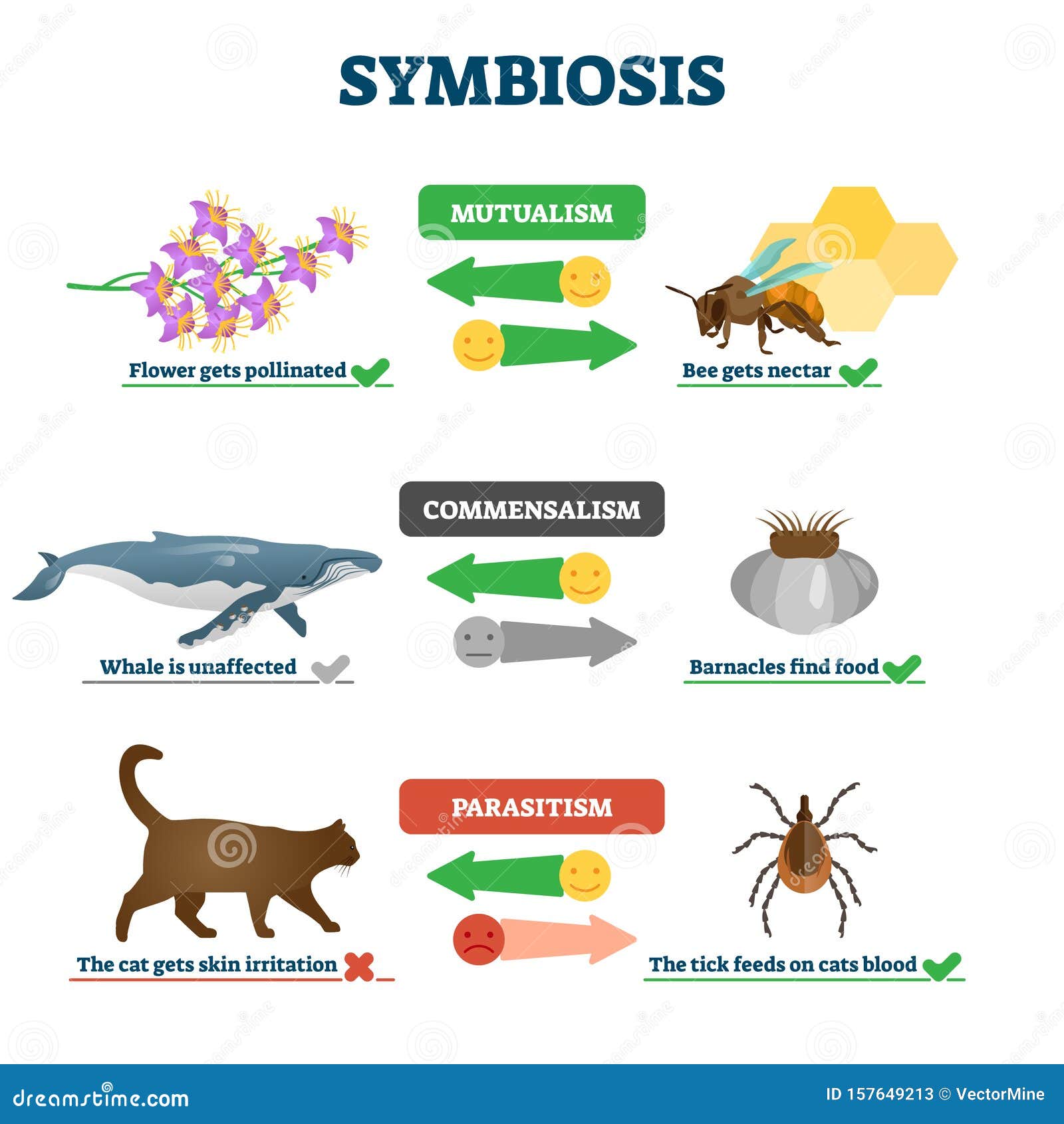
Mutualism Stock Illustrations 673 Mutualism Stock Illustrations

Mutualism Sea Anemone on Hermit Crab Drawing YouTube

Coevolution in a Mutualism Science illustration, Mutualism, Illustration

Mutualism Definition and Examples in Biology

Learn to Draw Mutualism Ghost Pipes and Tube Worms Sierra Club BC

Learn to Draw Mutualism Ghost Pipes and Tube Worms Sierra Club BC

Mutualism Drawing by Barima Andrew Saatchi Art
Web Mutualism Examples Show Unique Relationships Where Organisms Work Together For Mutual Benefit.
Here, You Might Spot A Group Of Clownfish Swimming In A Bed Of Sea Anemones.
Web Here It Is Essential To Differentiate Commensalism From Mutualism, Parasitism, And Amensalism.
It Is A Form Of Symbiosis That Organisms Develop For Any Of A Number Of Reasons, Including A.
Related Post: