Mercantilism Drawing, Identify the major criticisms of mercantilism;
Mercantilism Drawing - Web mercantilism was a form of economic nationalism that sought to increase the prosperity and power of a nation through restrictive trade practices. Web mercantilism is an economic theory and policy practised during canada’s colonial periods. Web mercantilism is an economic theory that advocates government regulation of international trade to generate wealth and strengthen national power. Web the cartoon illustrates the theory of mercantilism. Adam smith coined the term “mercantile system” to describe the system of political economy that sought to enrich the country by restraining imports and encouraging exports. This system dominated western european. Merchants and the government work together to reduce the trade deficit and create a trade surplus. Discuss the basic principles of mercantilism: The theory of mercantilism holds that there is a fixed amount of wealth in the world. A nation’s wealth is thus dependent on exporting (selling to other countries) more than it imports (buying from others). Option c is correct according to the theory of mercantilism. Its goal was to increase the supply of a state's. It was the economic counterpart of political absolutism. Mercantilism is theory of increasing gold reserves, restricting imports and protecting domestic economy. Web mercantilism was a doctrine prioritizing favourable trade balance, promoting exports and limiting imports through protectionism and monopolistic practices. Web mercantilism was a doctrine prioritizing favourable trade balance, promoting exports and limiting imports through protectionism and monopolistic practices. Web mercantilism is an economic practice by which governments used their economies to augment state power at the expense of other countries. To that end, it encourages colonialism, taxes, and subsidies on commercial products. The belief that a country's wealth and. Web the basis of mercantilism was the notion that national wealth is measured by the amount of gold and silver a nation possesses. Draw a diagram in the space below that shows how mercantilism worked. He prohibited the export of money, levied high tariffs on foreign manufactures, and gave liberal bounties to encourage french shipping. Web describe the theory of. Explain the role of colonies in mercantilism; Web mercantilism, the gold standard for western european countries between the 16th and late 18th centuries, was an economic system in which countries put a limit on how many imports can be brought into the country, while simultaneously encouraging as many exports as possible. Colonial empires such as those of england, france, and. Mercantilism held that only a limited amount of wealth, as measured in gold and silver bullion, existed in the world. Web as a practical politician intent on the welfare of the middle class to which he belonged, mercantilism was the most convenient method of attaining his end. Web mercantilism is an economic strategy intended to increase an economy's exports while. Web mercantilism is an economic strategy intended to increase an economy's exports while reducing its imports. The success of spain and portugal in establishing settlements in the americas, and more importantly, the profits they derived from those settlements, inspired other european nations to emulate them. Web as a practical politician intent on the welfare of the middle class to which. Web as a practical politician intent on the welfare of the middle class to which he belonged, mercantilism was the most convenient method of attaining his end. Mercantilism held that only a limited amount of wealth, as measured in gold and silver bullion, existed in the world. Web describe the theory of mercantilism; Adam smith coined the term “mercantile system”. M ercantilism is economic nationalism for the purpose of building a wealthy and powerful state. Option c is correct according to the theory of mercantilism. Web mercantilism is the name given to the economic doctrines and practices of major trading nations roughly from the fifteenth through the eighteenth centuries. It was the economic counterpart of political absolutism. Web mercantilism is. Web define mercantilism as an economic theory that was popular in europe from the 16th to the 18th century. Web as a practical politician intent on the welfare of the middle class to which he belonged, mercantilism was the most convenient method of attaining his end. He prohibited the export of money, levied high tariffs on foreign manufactures, and gave. Governments sought to ensure that exports exceeded imports and to accumulate wealth in the form of bullion (mostly gold and silver). Option c is correct according to the theory of mercantilism. Web mercantilism is an economic theory and policy practised during canada’s colonial periods. Web mercantilism, the gold standard for western european countries between the 16th and late 18th centuries,. It was the economic counterpart of political absolutism. Web mercantilism is an economic theory that advocates government regulation of international trade to generate wealth and strengthen national power. Web define mercantilism as an economic theory that was popular in europe from the 16th to the 18th century. The belief that a country's wealth and power were determined by the amount of gold and silver it possessed. Merchants and the government work together to reduce the trade deficit and create a trade surplus. Option c is correct according to the theory of mercantilism. A nation’s wealth is thus dependent on exporting (selling to other countries) more than it imports (buying from others). Web the cartoon illustrates the theory of mercantilism. Web the first writer to outline the modern concept of mercantilism, in 1776, smith launched a fierce denunciation of mercantilism and the implementation of mercantilist ideas, designed to benefit the merchant class and the government. The theory of mercantilism holds that there is a fixed amount of wealth in the world. He prohibited the export of money, levied high tariffs on foreign manufactures, and gave liberal bounties to encourage french shipping. Web mercantilism was a doctrine prioritizing favourable trade balance, promoting exports and limiting imports through protectionism and monopolistic practices. Explain the role of colonies in mercantilism; Web the basis of mercantilism was the notion that national wealth is measured by the amount of gold and silver a nation possesses. Web in adam smith’s seminal work an inquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of nations (1776), he rejects the basic tenets of mercantilism and argues that the division of labor and the. Web mercantilism, the gold standard for western european countries between the 16th and late 18th centuries, was an economic system in which countries put a limit on how many imports can be brought into the country, while simultaneously encouraging as many exports as possible.
Mercantilism illustration World history lessons, Teaching us history
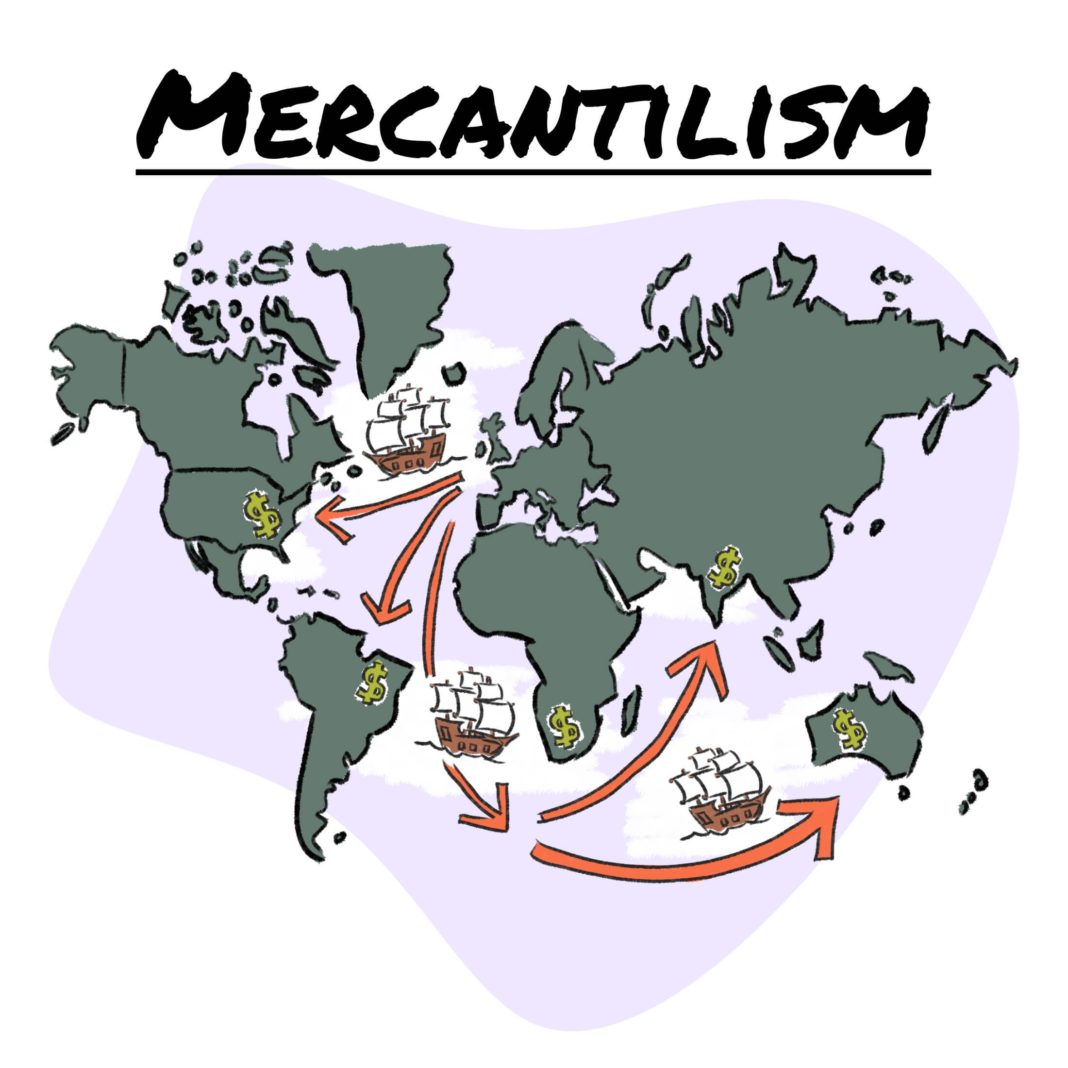
Merkantilizm 1618. Yüzyıllar Arası Ticarete Bakış Stratejik Ortak
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/maxresdefault2-a4bf74cf1bf74519b4384a5ef76d8dd6.jpg)
Mercantilism
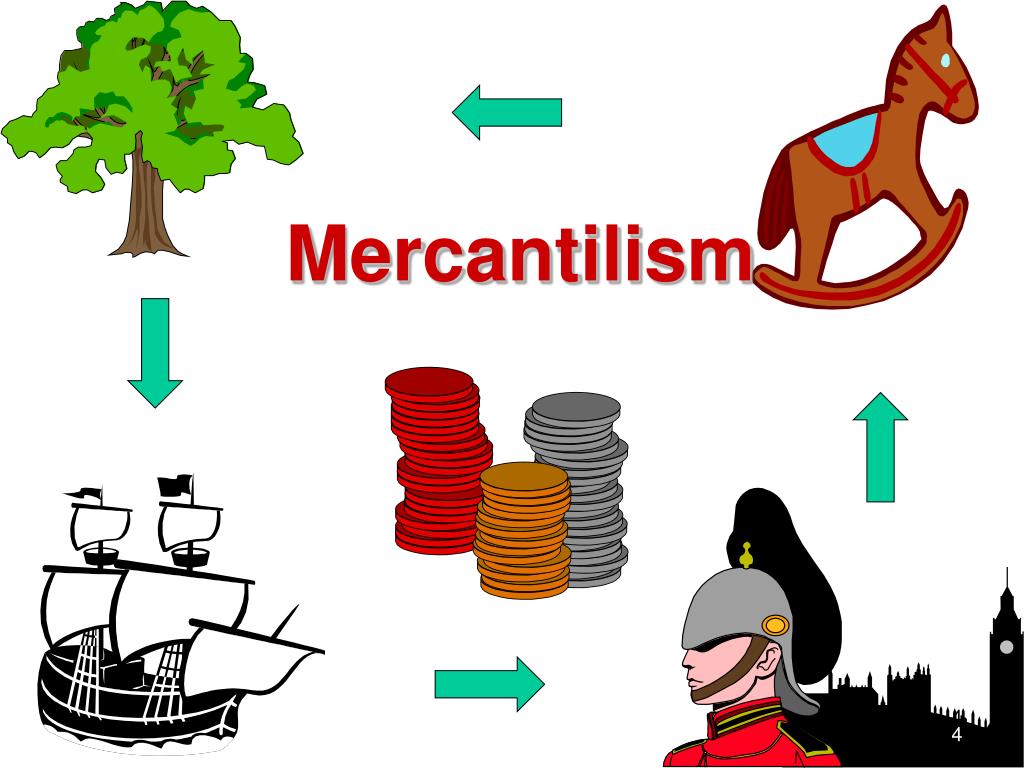
PPT Colonial Life PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6890028

Mercantilism A New Path To Wealth Through Imperfect Competition

Mercantilism
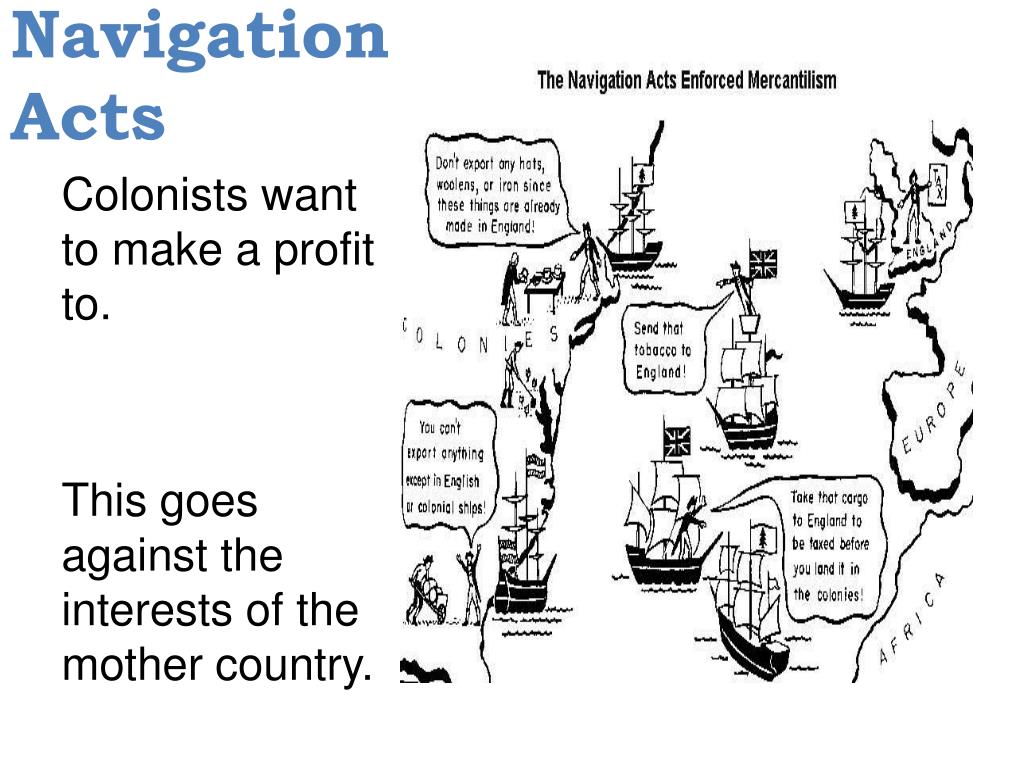
PPT Mercantilism PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2578378

Mercantilism vector illustration. Labeled economic policy explanation

Mercantilism Cartoon Flow Chart Canadian history, History cartoon

Mercantilism, Definition, Summary, Significance, Colonial America, APUSH
Web Mercantilism Is The Name Given To The Economic Doctrines And Practices Of Major Trading Nations Roughly From The Fifteenth Through The Eighteenth Centuries.
Web Mercantilism Is An Economic System Wherein Nations Established Colonies In Order To Gain Access To Natural Resources.
These Nations Then Sent These Resources Back To The Home Nation For The Betterment Of The Mother Country.
The Success Of Spain And Portugal In Establishing Settlements In The Americas, And More Importantly, The Profits They Derived From Those Settlements, Inspired Other European Nations To Emulate Them.
Related Post: