Meiosis Stages Drawing, Web there are two stages or phases of meiosis:
Meiosis Stages Drawing - Web describe and draw the key events and stages of meiosis that lead to haploid gametes. Web process of reduction division. 23k views 3 years ago biology diagrams (class 11 & 12) thanks for watching! As it enters this prophase, each chromosome consists of two tightly joined sister chromatids. Web steps of meiosis. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i and meiosis ii. Web stages/phases of meiosis. The gametes can then meet, during reproduction, and fuse to create a new zygote. Web animation of the stages of meiosis. Web steps of meiosis. Here, the chromosomes begin to condense. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i and meiosis ii. During meiosis, four daughter cells are produced, each of which are haploid (containing half as many chromosomes as the parent cell). Web animation of the stages of meiosis. Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. It is visibly obvious that replication has not occurred. Web the diagram of meiosis along with the explanation of its different stages is given below in detail. Web meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the chromosomes in the nucleus of the diploid cell. Each round. Prophase i is divided into five different stages: Instead of chromatids splitting at the centromere, homologous chromosome pairs (now shuffled by crossing over) move along the spindle fibers to opposite poles. Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. Web this color diagram illustrates the stages of meiosis, which is a type of cell division that results. Web process of reduction division. Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. • meiosis is not a cycle like mitosis. Web there are six stages within each of the divisions, namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. As in mitosis, the cell grows during g 1 phase, copies all of its chromosomes during s phase, and prepares for division during g 2 phase. This is the stage where genetic recombination may occur (via crossing over). Web process of reduction division. Each. Web meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the chromosomes in the nucleus of the diploid cell. This is the stage where genetic recombination may occur (via crossing over). Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. It is visibly obvious that replication has not occurred. Web by regina bailey. Homologous paternal and maternal chromosomes pair up along the midline of the cell. Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. It is visibly obvious that replication has not occurred. The chromosomes coil up, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, and the centrosomes begin moving apart. Web animation of the stages of meiosis. Web animation of the stages of meiosis. Homologous paternal and maternal chromosomes pair up along the midline of the cell. Here, the chromosomes begin to condense. The cell pinches and divides. Each stage includes a period of nuclear division or karyokinesis and a cytoplasmic division or cytokinesis. Events that occur during prophase of mitosis also occur during prophase i of meiosis. Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. Each stage includes a period of nuclear division or karyokinesis and a cytoplasmic division or cytokinesis. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material,. Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. Here, the chromosomes begin to condense. Web the diagram of meiosis along with the explanation of its different stages is given below in detail. In this article, we will look at the stages of meiosis and consider its significance in disease. Each stage includes a period of nuclear. Meiosis i encompasses four stages: Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. Web steps of meiosis. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes, or sex cells. Web meiosis starts with a diploid cell (a cell with two sets of chromosomes) and ends up with four haploid cells (cells with only one set of chromosomes), which are called gametes (eggs and sperm). Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. Web meiosis involves two successive stages or phases of cell division, meiosis i and meiosis ii. As in mitosis, the cell grows during g 1 phase, copies all of its chromosomes during s phase, and prepares for division during g 2 phase. Events that occur during prophase of mitosis also occur during prophase i of meiosis. Web meiosis is dominated by prophase of meiotic division i, which can occupy 90% or more of the total meiotic period. It is visibly obvious that replication has not occurred. Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i and meiosis ii. Web there are six stages within each of the divisions, namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis.![[DIAGRAM] The 8 Stages Of Meiosis Diagram And Label](http://tmsseventhgradeteam.weebly.com/uploads/5/8/1/6/58160795/meiosis.gif)
[DIAGRAM] The 8 Stages Of Meiosis Diagram And Label

Stages of meiosis vector illustration Meiosis, Educational

Drawing Meiosis BioNinja
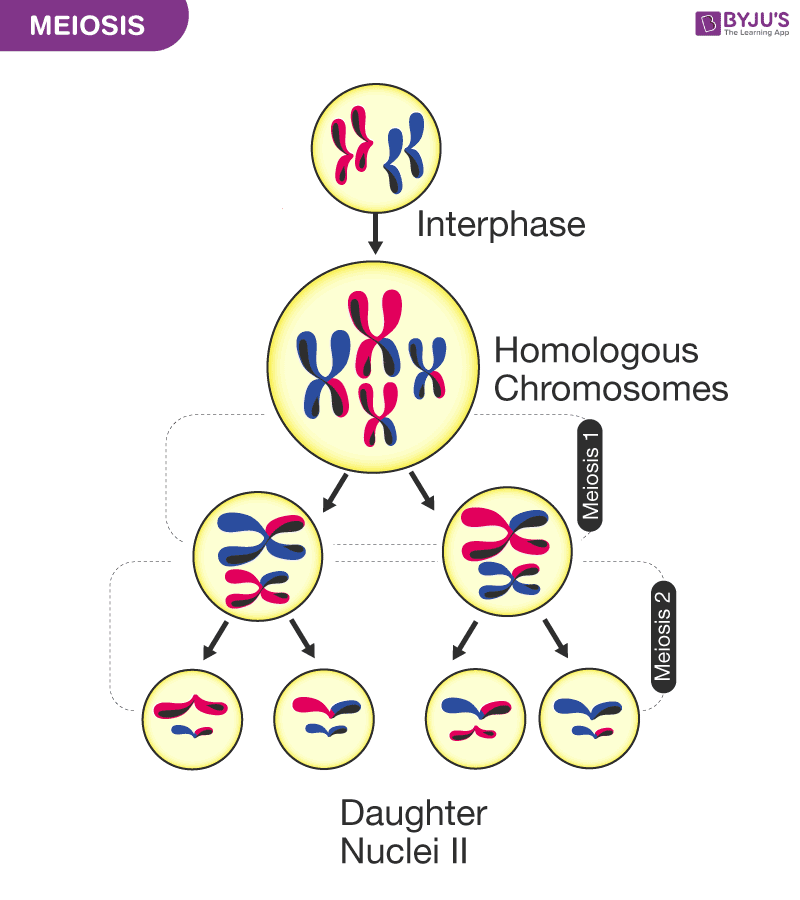
9 Stages Of Meiosis
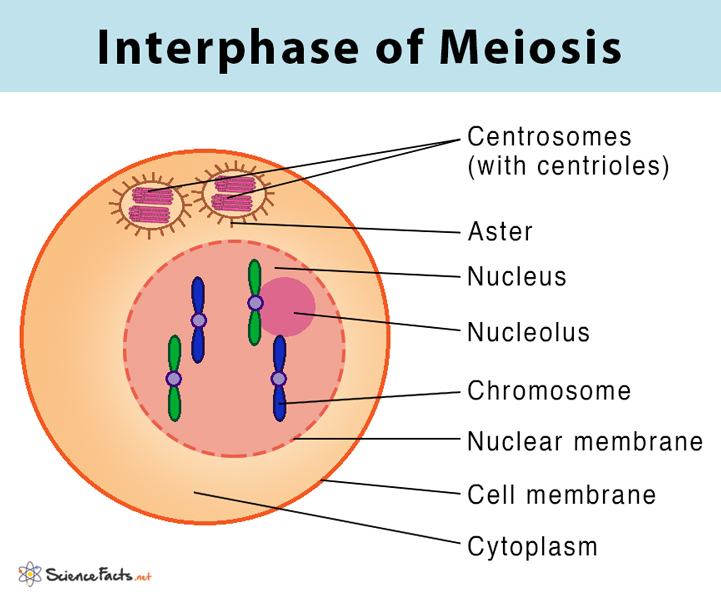
Meiosis Definition, Stages, & Purpose with Diagram
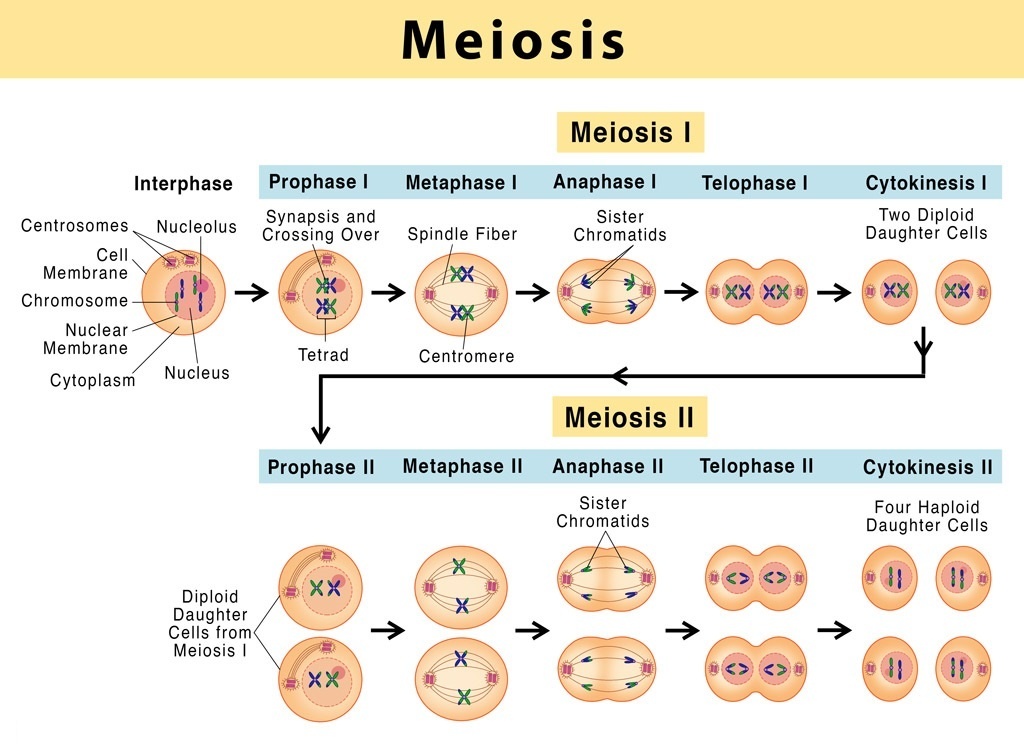
Phases of Meiotic cell division (Meiosis), Nanotechnology and cancer
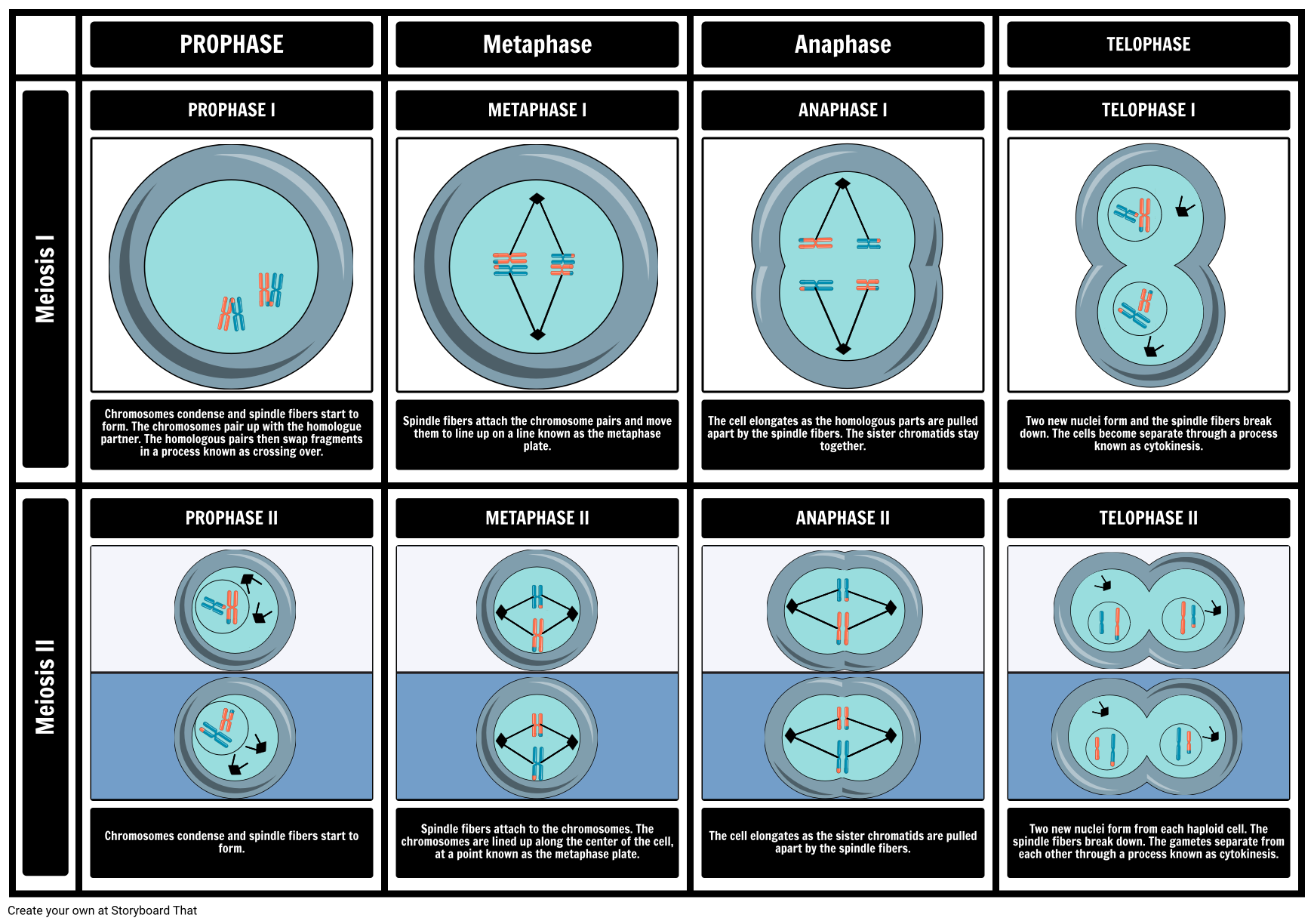
Stages of Meiosis 1 & 2 Free Diagram Activity

Basic Stages Of Meiosis Diagram

Meiosis, Stages, Meiosis vs Mitosis The Virtual Notebook
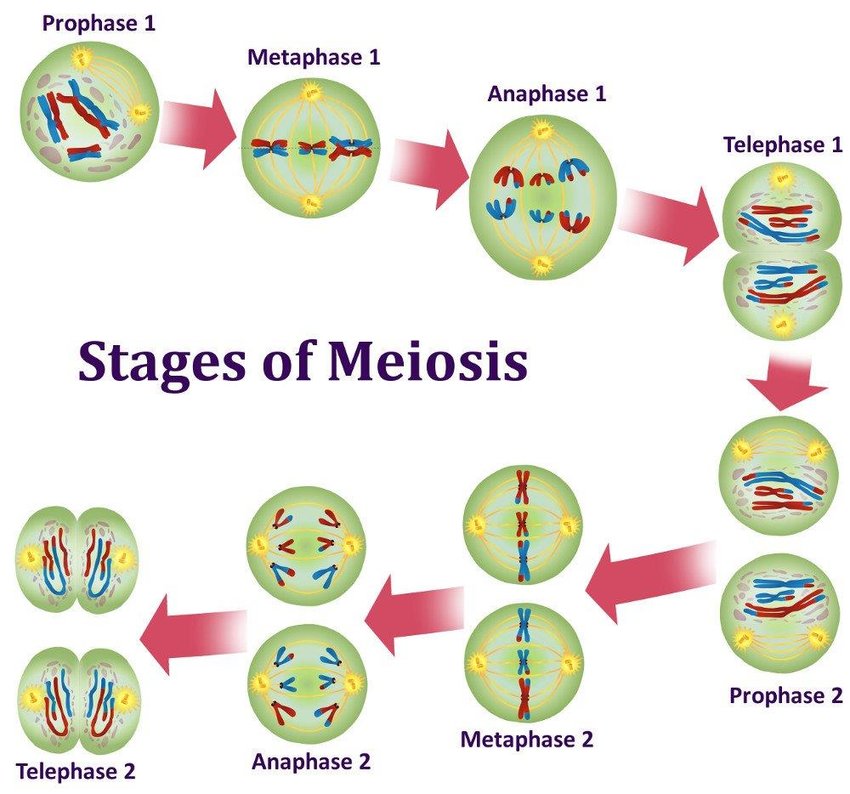
10 Stages Of Meiosis
Here, The Chromosomes Begin To Condense.
It Is Crucial For Sexual Reproduction In Eukaryotes.
Web Animation Of The Stages Of Meiosis.
In Metaphase I, Chromosomes Line Up.
Related Post: