Hypertonic Drawing, Describe the mechanisms of action of hypertonic saline and mannitol.
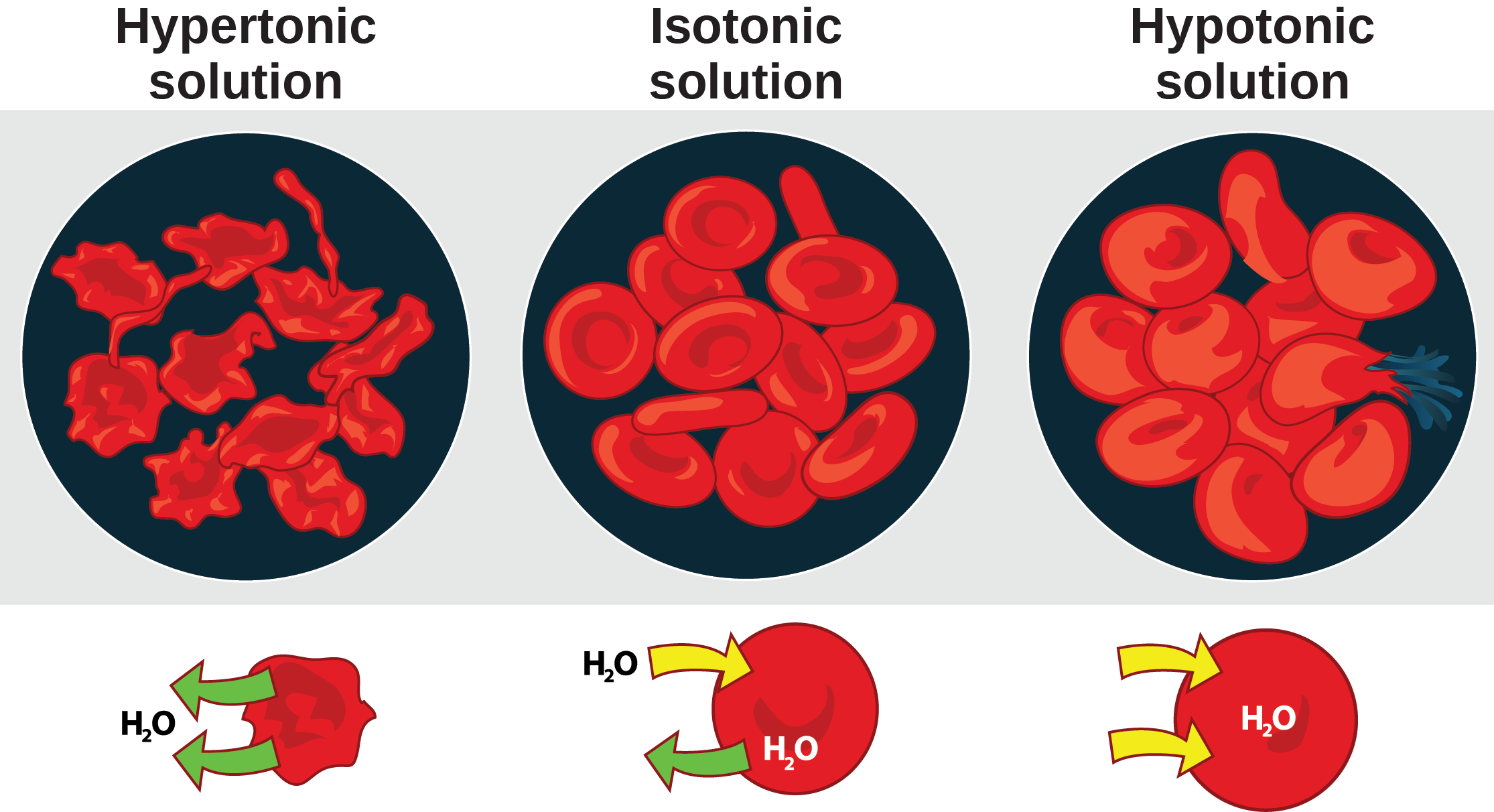
Hypertonic Drawing - The opposite solution, with a lower concentration or osmolarity, is known as the hypotonic solution. Web three terms—hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic—are used to describe whether a solution will cause water to move into or out of a cell: Hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions! In other words, a hypertonic solution is one in which there is a greater concentration or number of solute particles outside a membrane than there are inside it. Describe the mechanisms of action of hypertonic saline and mannitol. Whether a solution is hypertonic or not is measured by comparing the concentration of a solution with another, generally cell sap. Plant cells in a hypertonic solution can look like a pincushion because of what’s going on inside. Read this study guide to get a deep understanding of these types of solutes. Web hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions. Students will learn about isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions and how these solutions affect the movement of water molecules across the cell membrane. Hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions! Hypotonic hydration swells cells by promoting water intake, whereas hypertonic hydration shrinks them by drawing water out. Hypotonic solutions, on the other hand, have a lower solute concentration and cause water to move into cells, potentially causing them to swell or burst. Whether a solution is hypertonic or not is measured by comparing the concentration. This type of solution exerts greater osmotic pressure and draws water out of cells placed in it, potentially leading to cell shrinkage or crenation. Plant cells in a hypertonic solution can look like a pincushion because of what’s going on inside. Web this video is a review of hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic solutions, how they lead to plasmolysis, cytolysis and. Students will learn about isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions and how these solutions affect the movement of water molecules across the cell membrane. Web a hypertonic solution contains a higher concentration of solutes compared to another solution. Read this study guide to get a deep understanding of these types of solutes. This is clearly seen in red blood cells undergoing. Web hypertonic solutions can make it easier for the kidneys to remove excess water from your patient’s body. Web hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions (tonicity). Web hypertonic solution the solution whose osmotic pressure is higher than that of the other is called a hypertonic solution. Web hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration and cause water to move out of. Web hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration than inside the cell. In a hypotonic solution, water rushes into the cell causing it to expand or even burst. This biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction. Web hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions. Students will learn about isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions and how these solutions affect the movement of water. As a result the cell would shrink in what is called plasmolysis. Web when placed in a hypertonic solution, a red blood cell will lose water and undergo crenation (shrivel). Web hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions (tonicity). Hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions! Web hypertonic refers to a solution with higher osmotic pressure than another solution. Hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions! Hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions! Web need help in understanding hypotonic vs hypertonic, and isotonic solutions? In other words, a hypertonic solution is one in which there is a greater concentration or number of solute particles outside a membrane than there are inside it. Web hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration and cause water. Web hypertonic solution the solution whose osmotic pressure is higher than that of the other is called a hypertonic solution. In an isotonic solution, there is no net flow of water, keeping the cell stable. A hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solute than another solution, meaning water will flow out of it. As a result the cell would. Web this video is a review of hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic solutions, how they lead to plasmolysis, cytolysis and dynamic equilibrium. Web when placed in a hypertonic solution, a red blood cell will lose water and undergo crenation (shrivel). Hypotonic hydration swells cells by promoting water intake, whereas hypertonic hydration shrinks them by drawing water out. Web a hypertonic solution. Students will learn about isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions and how these solutions affect the movement of water molecules across the cell membrane. Web three terms—hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic—are used to describe whether a solution will cause water to move into or out of a cell: This causes water to rush out making the cell wrinkle or shrivel. If a. Students will learn about isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions and how these solutions affect the movement of water molecules across the cell membrane. Describe the mechanisms of action of hypertonic saline and mannitol. Hypertonic, hypotonic and isotonic solutions! Web need help in understanding hypotonic vs hypertonic, and isotonic solutions? This biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction. Web three terms—hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic—are used to describe whether a solution will cause water to move into or out of a cell: As a result the cell would shrink in what is called plasmolysis. Web a hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute than another solution, meaning water will flow into it. Web hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions (tonicity). Whether a solution is hypertonic or not is measured by comparing the concentration of a solution with another, generally cell sap. Web when placed in a hypertonic solution, a red blood cell will lose water and undergo crenation (shrivel). Web a hypertonic solution causes cells to shrink as water moves out of the cell to balance solute concentrations. Outline the route of administration and appropriate dosing for hypertonic fluids. This causes water to rush out making the cell wrinkle or shrivel. Hypotonic hydration swells cells by promoting water intake, whereas hypertonic hydration shrinks them by drawing water out. Animal cells tend to do best in an isotonic environment, where the flow of water in and out of the cell is occurring at equal rates.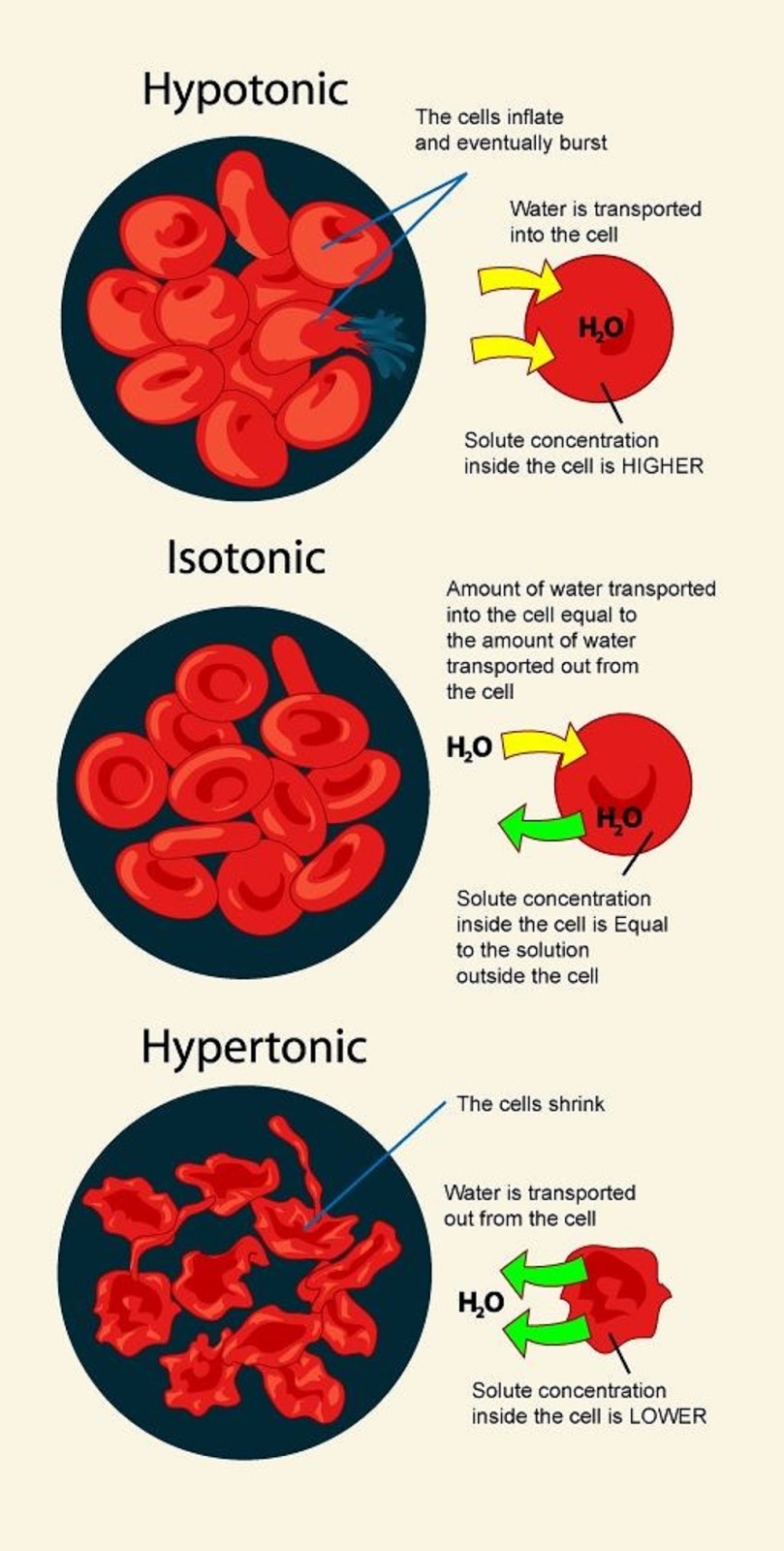
Medical and Health Science Hypotonic, Isotonic, Hypertonic Solution
Osmoregulation and Osmotic Balance OpenStax Biology 2e

Hypertonic Hypotonic And Isotonic Cells

Types of solutionshypertonic hypotonic and isotonic explained YouTube

Iso, Hypo, and Hypertonic Solutions Diagram Quizlet

Illustration showing the effect of hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic

effets de hypertonique, hypotonique et istonique solutions à rouge du

Animal Cell In Hypertonic Solution

Hypertonic Diagram

Hypertonic, Hypotonic, & Isotonic Diagram Quizlet
Web Hypertonic Solutions Have A Higher Solute Concentration And Cause Water To Move Out Of Cells, Potentially Leading To Cell Shrinkage.
Web Hypertonic Solution The Solution Whose Osmotic Pressure Is Higher Than That Of The Other Is Called A Hypertonic Solution.
In Other Words, If There Are More Solutes Outside The Cell Than Inside, Water Will Move Out.
In An Isotonic Solution, There Is No Net Flow Of Water, Keeping The Cell Stable.
Related Post: