Drawing Stages Of Meiosis, Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i and meiosis ii.
Drawing Stages Of Meiosis - There are two divisions in meiosis; As in mitosis, the cell grows during g 1 phase, copies all of its chromosomes during s phase, and prepares for division during g 2 phase. Recall that homologous chromosomes separate during meiosis i (a reductional division) and that sister chromatids separate during meiosis ii (an equational division). Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Web drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. Web thanks for watching! It will also help you understand the. Web this video explains the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells and also how to draw the stages. This results in 1/2 as many chromosomes per cell. When cells commit to meiosis, dna replicates. Web within each division there are the following stages: Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Web drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. The g 1 phase, which is also called the first gap. When cells commit to meiosis, dna replicates. Web meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The g 1 phase, which is also called the first gap phase, is the first phase of the interphase and is. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web. Web there are two stages or phases of meiosis: Web meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the chromosomes in the nucleus of the diploid cell. Each round of division contains a period of karyokinesis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division). Meiosis i and meiosis ii. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Web meiosis involves only one round of dna replication where each chromosome replicates to form sister chromatids. Web meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. This division is like mitosis; Web within each division there are the following stages: Meiosis i and. Web here’s a breakdown of the stages of meiosis and a look at what happens: Web meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The first division is meiosis i: Web this video explains the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of. Recall that homologous chromosomes separate during meiosis i (a reductional division) and that sister chromatids separate during meiosis ii (an equational division). Web meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. Web in meiosis i, cells go through four phases: It starts with. Dna replication has already occurred so each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined together by a centromere. Web stages/phases of meiosis. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. It will also help you understand the. Dna condenses and becomes visible as chromosomes. Web here’s a breakdown of the stages of meiosis and a look at what happens: Web in each round of division, cells go through four stages: Web meiosis involves two successive stages or phases of cell division, meiosis i and meiosis ii. Web meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the g 1, s, and g 2 phases, which. The number of chromosomes does not get reduced. Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In humans, there are 46 chromosomes or 46 pairs of chromatids. Web in each round of division, cells go through four stages: Web prophase i is divided into five different stages: It starts with prophase ii, where the nuclear envelope dissolves and chromosomes condense. When cells commit to meiosis, dna replicates. Web there are two stages or phases of meiosis: Web in each round of division, cells go through four stages: Web in each round of division, cells go through four stages: Homologous paternal and maternal chromosomes pair up along the midline of the cell. Web in each round of division, cells go through four stages: Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. Web prophase i is divided into five different stages: It starts with prophase ii, where the nuclear envelope dissolves and chromosomes condense. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The period prior to the synthesis of dna. The g 1 phase, which is also called the first gap phase, is the first phase of the interphase and is. Then, in metaphase ii, chromosomes line up along the cell's middle. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. Web thanks for watching! As in mitosis, the cell grows during g 1 phase, copies all of its chromosomes during s phase, and prepares for division during g 2 phase. The g 1 phase, which is also called the first gap phase, is the first phase of the interphase and is focused on cell growth. Web here’s a breakdown of the stages of meiosis and a look at what happens:
Stages of meiosis vector illustration Meiosis, Educational

Stages of Meiosis BioNinja

Basic Stages Of Meiosis Diagram

What is meiosis? Facts
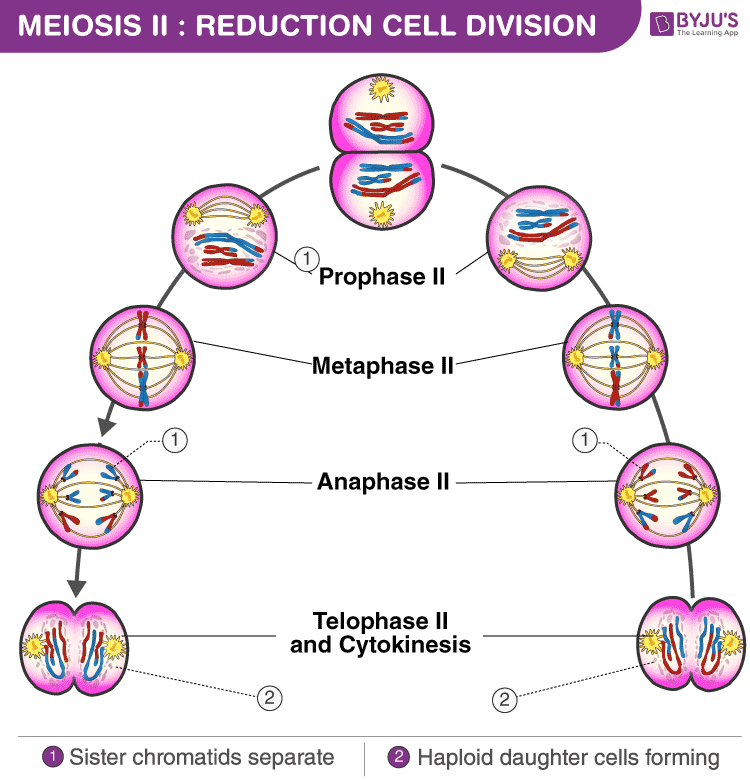
Meiosis Phases Explore the various stages of meiosis

Meiosis!

Meiosis 1 Stages Diagram

meiosis cytology

Meiosis, Stages, Meiosis vs Mitosis The Virtual Notebook
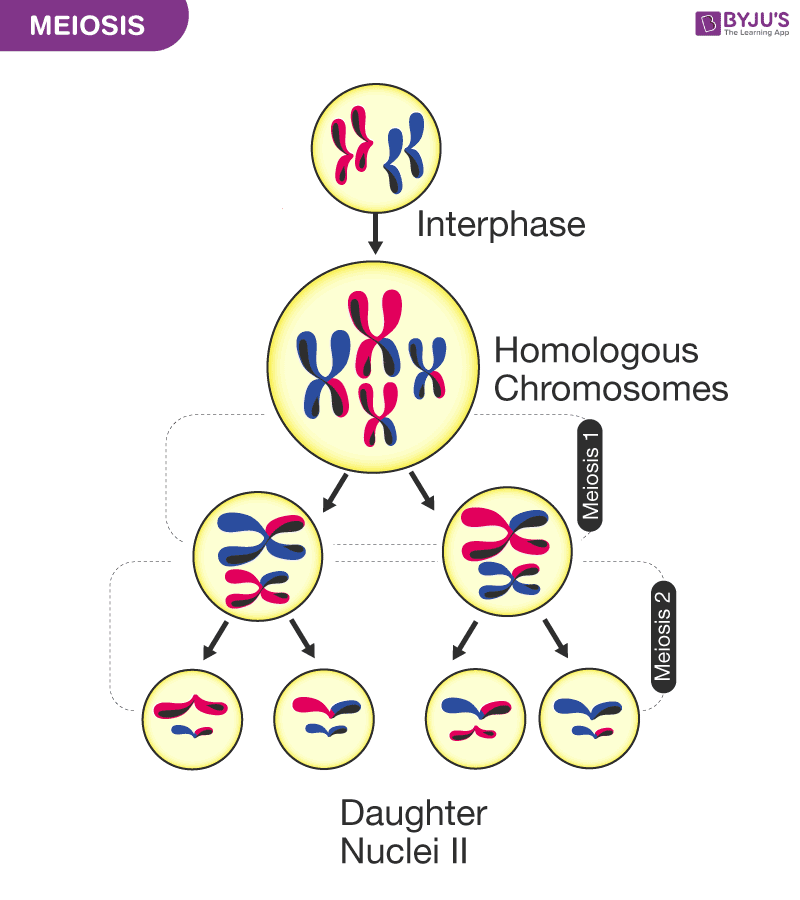
9 Stages Of Meiosis
Web Meiosis Is Preceded By An Interphase Consisting Of The G 1, S, And G 2 Phases, Which Are Nearly Identical To The Phases Preceding Mitosis.
Recall That Homologous Chromosomes Separate During Meiosis I (A Reductional Division) And That Sister Chromatids Separate During Meiosis Ii (An Equational Division).
Web Within Each Division There Are The Following Stages:
Web Meiosis Begins With Prophase I And The Contraction Of The Chromosomes In The Nucleus Of The Diploid Cell.
Related Post: