Drawing Of Charles Law, This relationship, illustrated in part (b) in figure \(\pageindex{3}\) is often referred to as charles’s law and is stated mathematically as
Drawing Of Charles Law - Robert boyle conducted an experiment on gases to study the deviation of its behaviour in changed physical conditions. Web charles's law , also known as the law of volumes, explains the relationship between the volume of an ideal gas and its absolute temperature under constant pressure. Web charles' law examines the relationship between the volume of a gas and its temperature. Web charles's law states that the volume (v) of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature (t) when pressure is kept constant. It was first stated by french scientist jacques charles in 1787. Web charle’s law states that the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure. Charles's law relates a gas's volume and temperature at constant pressure and amount. Web charles' law was formulated by the famous scientist jacques charles, less than 2 centuries after boyle’s law, in 1800. This relationship, illustrated in part (b) in figure \(\pageindex{3}\) is often referred to as charles’s law and is stated mathematically as Web charles’s law implies that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. So, as the temperature decreases the particles have occupy a smaller volume if the pressure is to remain constant. Web charles' law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. The absolute temperature is temperature measured with the kelvin scale. Let’s assume you get the following data.. Web charles's law , also known as the law of volumes, explains the relationship between the volume of an ideal gas and its absolute temperature under constant pressure. Charles's law relates a gas's volume and temperature at constant pressure and amount. Web the behavior of gases can be modeled with gas laws. At constant pressure, the volume of a mass. Boyle's law relates a gas's pressure and volume at constant temperature and amount. There’s no duo that takes method dressing more seriously than zendaya and law roach. Web charles' law, also known as the law of volumes, describes how gases tend to expand when heated. Web charles’ law can be stated as follows: So, as the temperature decreases the particles. Web charles law is an ideal gas law that establishes a relation between volume and temperature at constant pressure. The volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure and directly proportional to its temperature and the amount of gas. At constant pressure, the volume of a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (in. At constant pressure, the volume of a mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (in degrees kelvin). In gas laws, temperatures must always be expressed in kelvins. The temperature must be measured with the kelvin scale. Web the behavior of gases can be modeled with gas laws. A modern statement of charles' law is: Web charles's law states that the volume of a given mass of gas varies directly with the absolute temperature of the gas when pressure is kept constant. Charles's law states that the volume of an ideal gas changes proportionally to the temperature of that gas, given that pressure and amount of gas present are held constant. This relationship, illustrated in. Web charle’s law states that the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure. There’s no duo that takes method dressing more seriously than zendaya and law roach. Web charles’ law is an experimental gas law that describes how gases expand when heated. Boyle showed that the volume of a sample of a. There’s no duo that takes method dressing more seriously than zendaya and law roach. It can be stated as: The relationship between the volume of a gas and temperature was observed by jacques charles in 1787. Web charles law is an ideal gas law that establishes a relation between volume and temperature at constant pressure. So you would do an. This relationship, illustrated in part (b) in figure \(\pageindex{3}\) is often referred to as charles’s law and is stated mathematically as Web charles's law states that the volume of a given mass of gas varies directly with the absolute temperature of the gas when pressure is kept constant. Web charles’s law or the law of volumes is an ideal gas. Web charles' law was formulated by the famous scientist jacques charles, less than 2 centuries after boyle’s law, in 1800. Web charles’ law can be stated as follows: The volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure and directly proportional to its temperature and the amount of gas. Charles's law relates a gas's volume and temperature at constant. Web charles' law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. In gas laws, temperatures must always be expressed in kelvins. There’s no duo that takes method dressing more seriously than zendaya and law roach. Boyle's law relates a gas's pressure and volume at constant temperature and amount. Web charles' law describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a fixed mass of gas that is held at a fixed pressure. The volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure and directly proportional to its temperature and the amount of gas. Web charles's law , also known as the law of volumes, explains the relationship between the volume of an ideal gas and its absolute temperature under constant pressure. It states that under a constant temperature when the pressure on a gas increases its volume decreases. Also known as the “law of volume,” this law states that volume. V 1 /t 1 = v 2 /t 2. Therefore, v ∝ t or, v = kt, p &. This relationship of direct proportion can be. The pressure is caused by the gas molecules bumping into the walls of the container; It was first stated by french scientist jacques charles in 1787. Charles’ law states that the volume occupied by a gas at constant pressure is proportional to its temperature. At constant pressure, the volume of a mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (in degrees kelvin).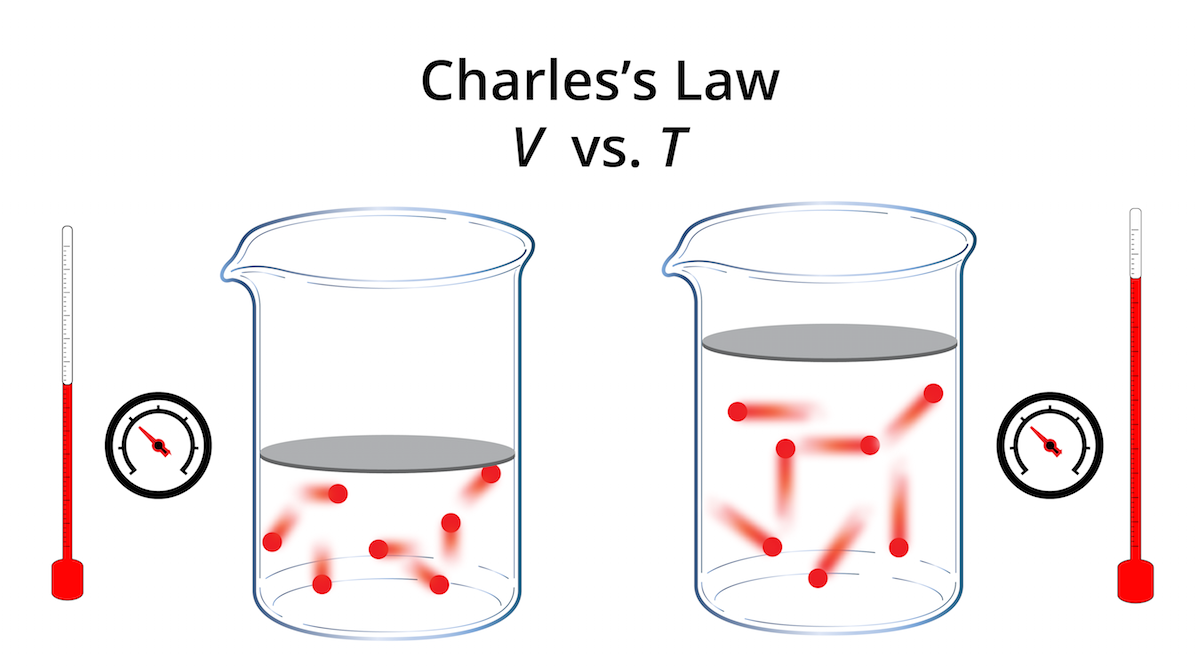
Properties of Gases Chemistry Visionlearning

Charles S Law. Relationship between Volume and Temperature Stock Vector

Charless Law Relationship Between Volume Temperature Stock Vector
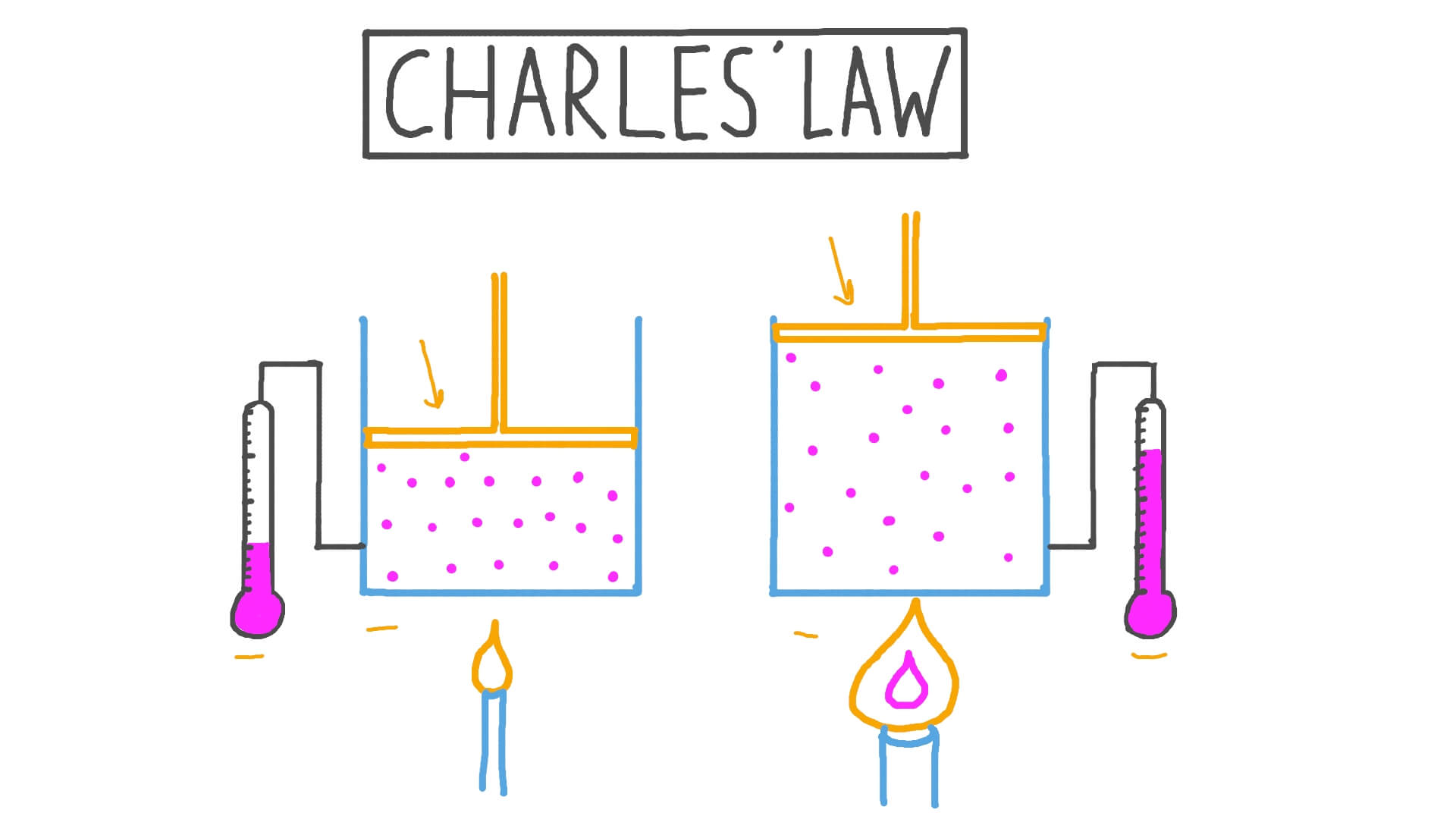
Unit 1 Behavior of Matter & Properties of Gases
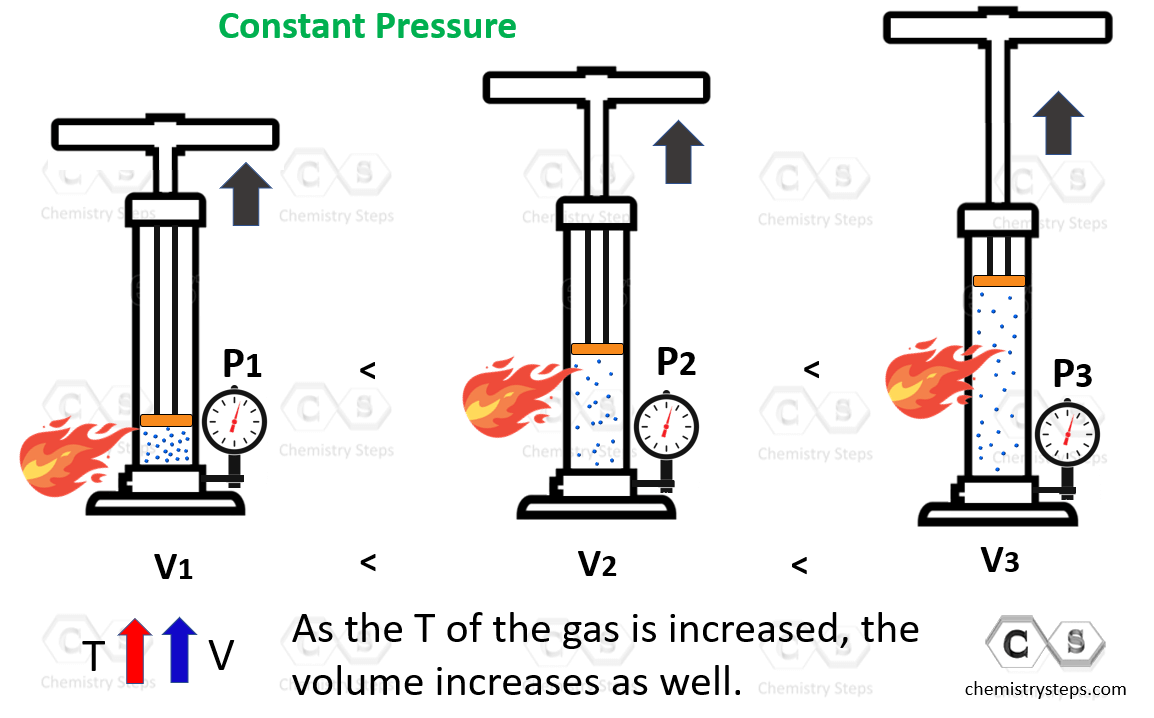
Charle’s Law Chemistry Steps
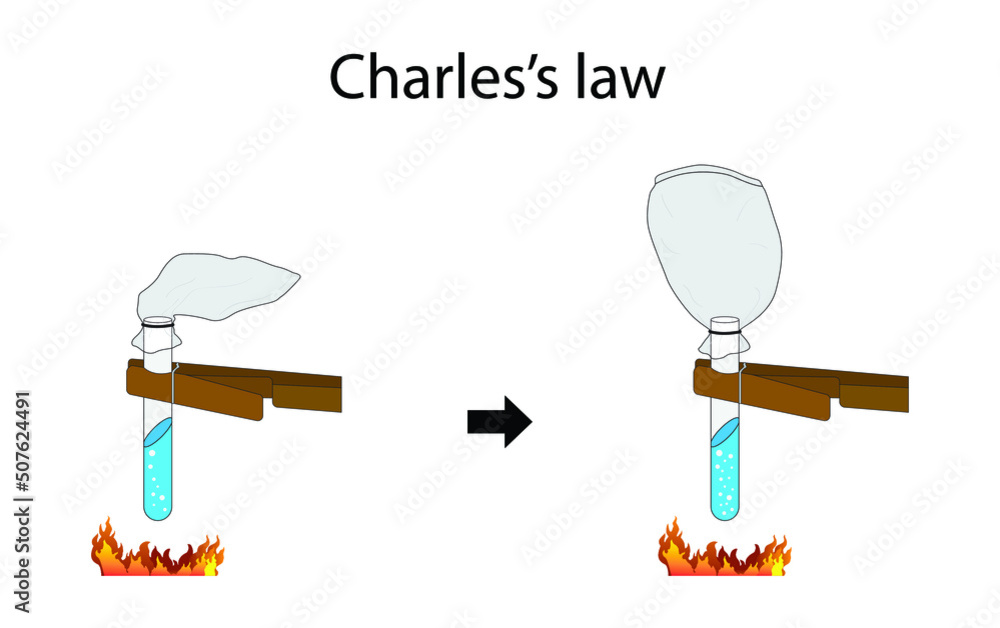
illustration of physics and chemistry, Charles' law is an experimental

Charles’ Law Statement, Formula, Examples, and Graph
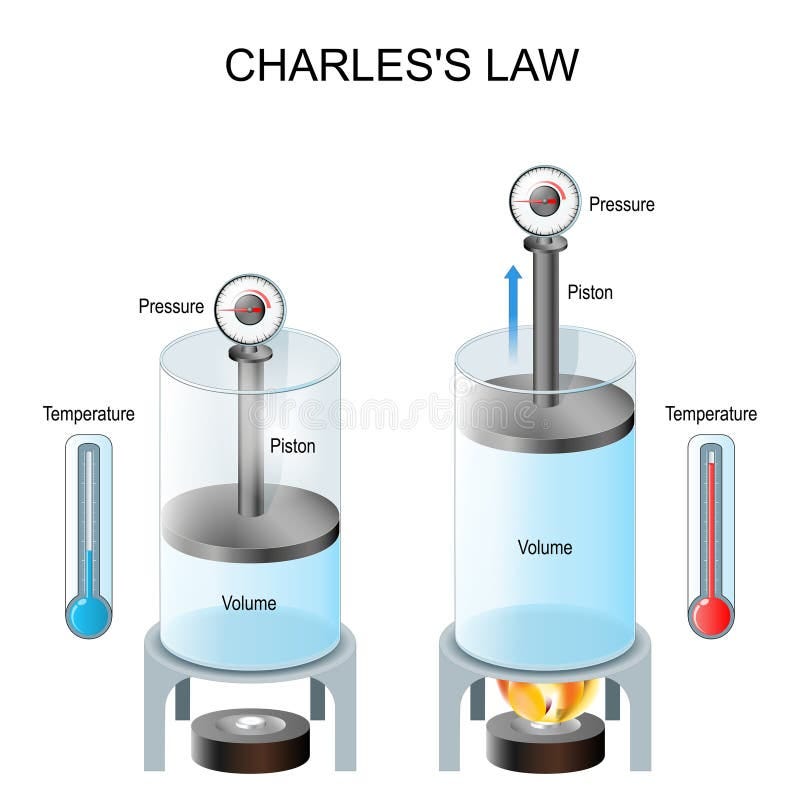
Charles law volume and temperature Teach Chemistry

Charles's Law Definition, Formula, Examples

Chemistry Charles's Law (Gas Laws) with 2 examples Charles law
At Constant Pressure The Volume Of A Given Mass Of A Gas Increases Or Decreases By 1/273 Of Its Volume At 0 O C For Every Degree Rise Or Fall In Temperature.
Doubling The Temperature Of A Gas Doubles Its Volume.
Web Charle’s Law States That The Volume Of An Ideal Gas Is Directly Proportional To The Absolute Temperature At Constant Pressure.
Web Charles' Law, Also Known As The Law Of Volumes, Describes How Gases Tend To Expand When Heated.
Related Post: