Drawing Of Cell Cycle, The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components:
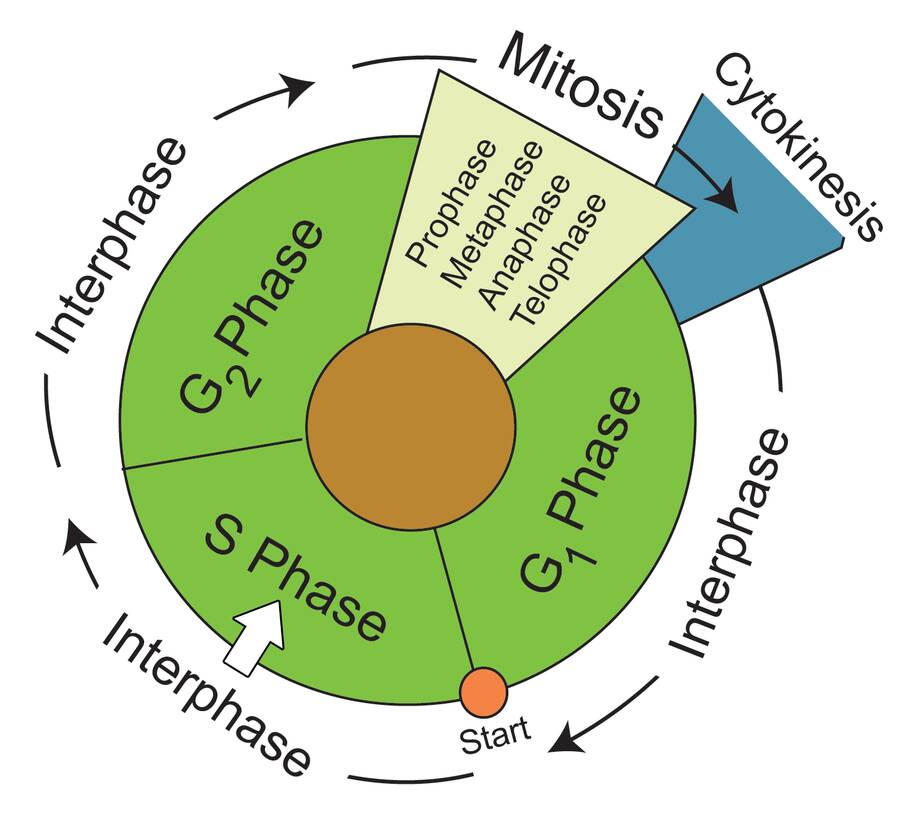
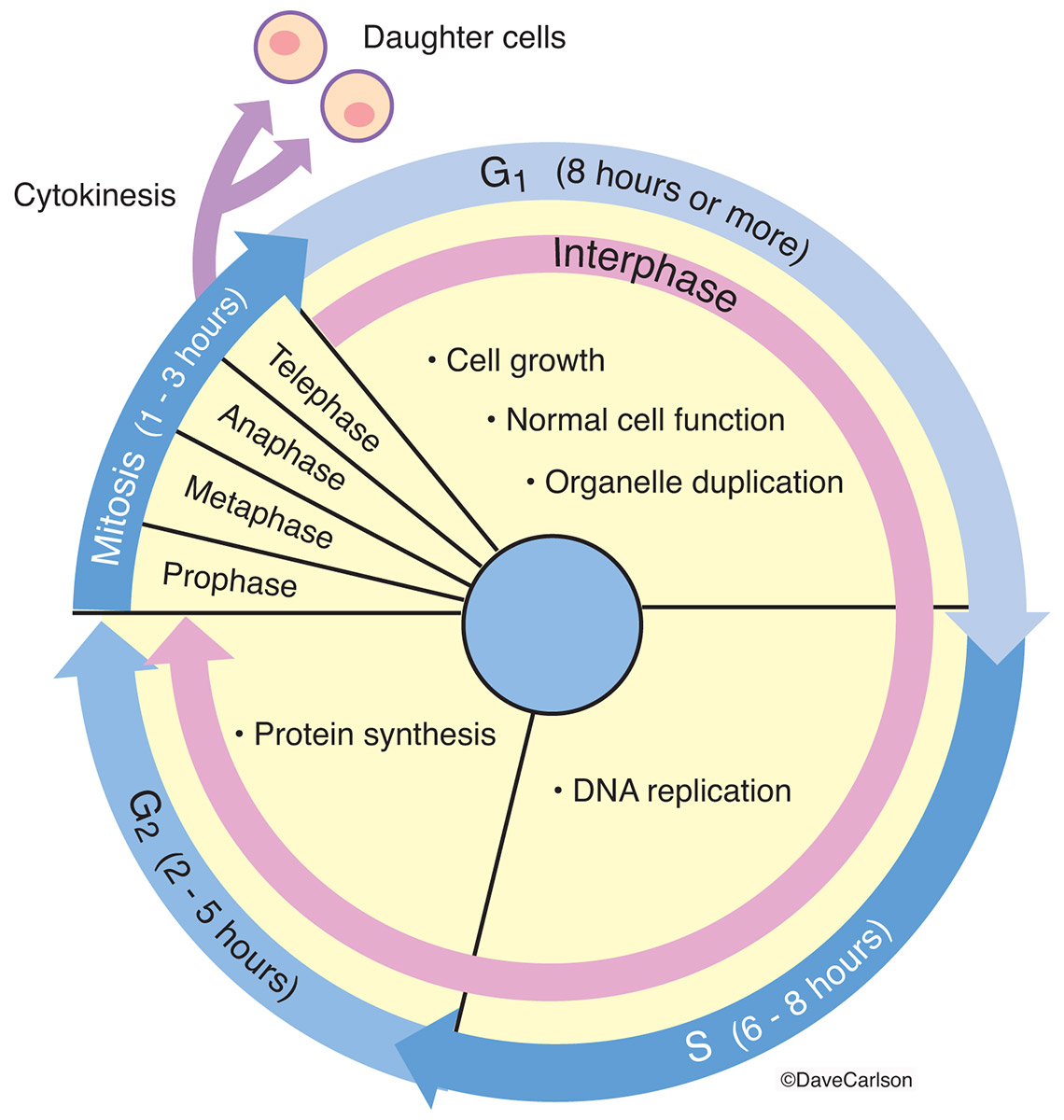
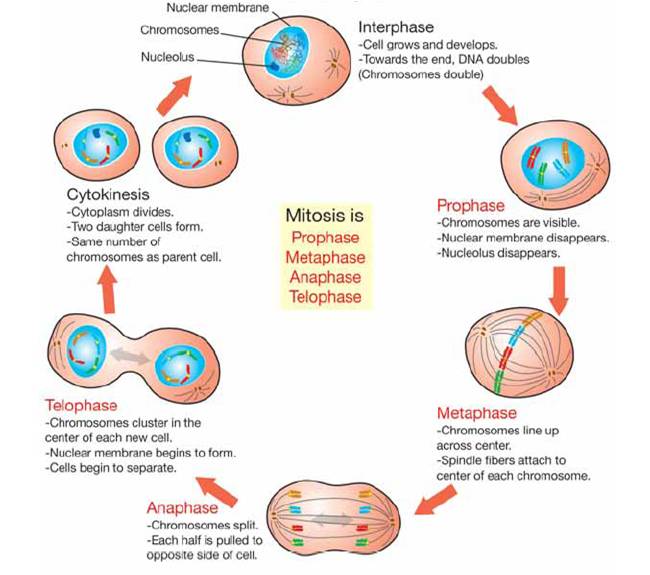
Drawing Of Cell Cycle - The cell cycle is divided into several phases; In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. Web the cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: Interphase is followed by the mitotic phase. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. Web what is the cell cycle? The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. This is when the cell grows and copies its dna before moving into mitosis. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. Web in eukaryotic. G2 (gap 2) phase 4. A cell cycle is thus a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. Interphase and mitosis (or the mitotic (m) phase). In interphase, a newly formed cell and its nucleus enquiring a series of changes before it becomes capable of division again. Web the cell. Cells divide during mitosis (m). Cells divide into new (daughter) cells through a series of events that take place in steps. In interphase, a newly formed cell and its nucleus enquiring a series of changes before it becomes capable of division again. Web in eukaryotic cells (having a cell nucleus) including animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells, the cell cycle. Web overview of the cell cycle phases. This video walks through drawing the stages of the cell cycle. Interactive radial gene expression diagram for a selected. The diagram of cell cycle labeled is given below: Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. The g 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. Charlotte schwenner, helmholtz. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. During interphase, the cell undergoes normal growth. This video walks through drawing the stages of the cell cycle. Web what is the cell cycle? Interphase, and the m phase that includes mitosis and cytokinesis. What is the difference between stem cells and cancer cells? Web the cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. As viewed in the microscope, the cell cycle is divided into two basic parts: A cell cycle is. Explain the similarities and differences of cancer cells and stem cells. A cell cycle is thus a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. (b) m phase (mitotic phase) (a) interphase. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. Cells divide into new (daughter). The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. Cellular growth and the preparation of cells for division between two successive cell divisions is called the cell cycle. In interphase, a newly formed cell and its nucleus. Web a typical eukaryotic cell cycle is illustrated by human cells in culture, which divide approximately every 24 hours. What is the difference between stem cells and cancer cells? Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Interactive radial gene expression diagram for a selected. Web in eukaryotic cells (having a cell nucleus) including animal, plant, fungal,. During interphase, the cell undergoes normal growth. G2 (gap 2) phase 4. A cell cycle is thus a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. After completing the cycle it either starts the process again from g1 or exits through g0. Web the cell cycle is composed of interphase (g₁, s, and g₂ phases), followed by the mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), and g₀ phase. Identify the characteristics of cytokinesis. The cycle begins at the end of each nuclear division and ends with the beginning of the next. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. The video quality is not the greatest but if you follow along i highlight some key features fo. Web an overview of the cell cycle. In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles followed by division of the cytoplasm. Interphase steps are the first gap phase (g 1 ), the synthesis phase (s), and the second gap phase (g 2 ). In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle.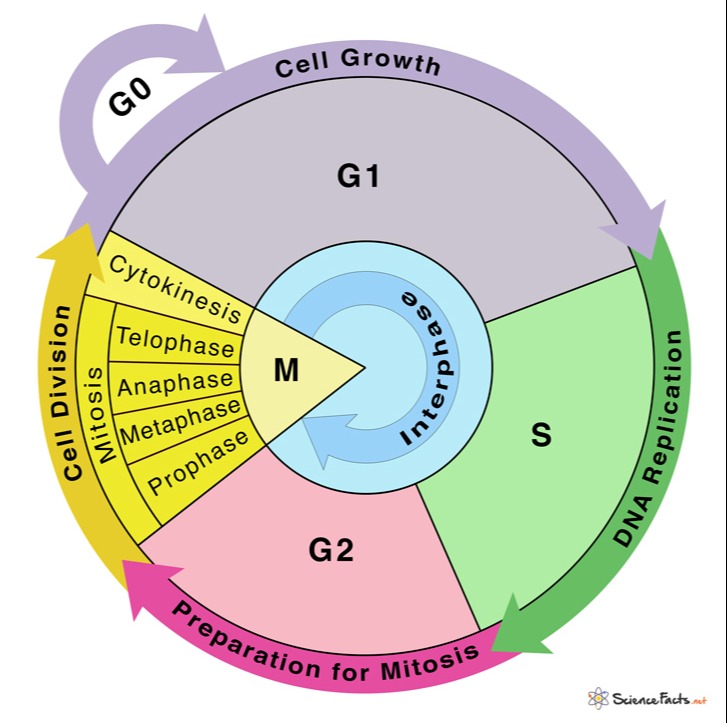
The Cell Cycle Study Guide Inspirit
Cell Biology, Mitosis Cell Cycle

Cell Division An Intro AmoebaMike
Phases Of Cell Cycle

Mitosis Cell Cycle Biology Notes Riset
The Cell Cycle Wonders of Life Science

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology

Cell Cycle Biology
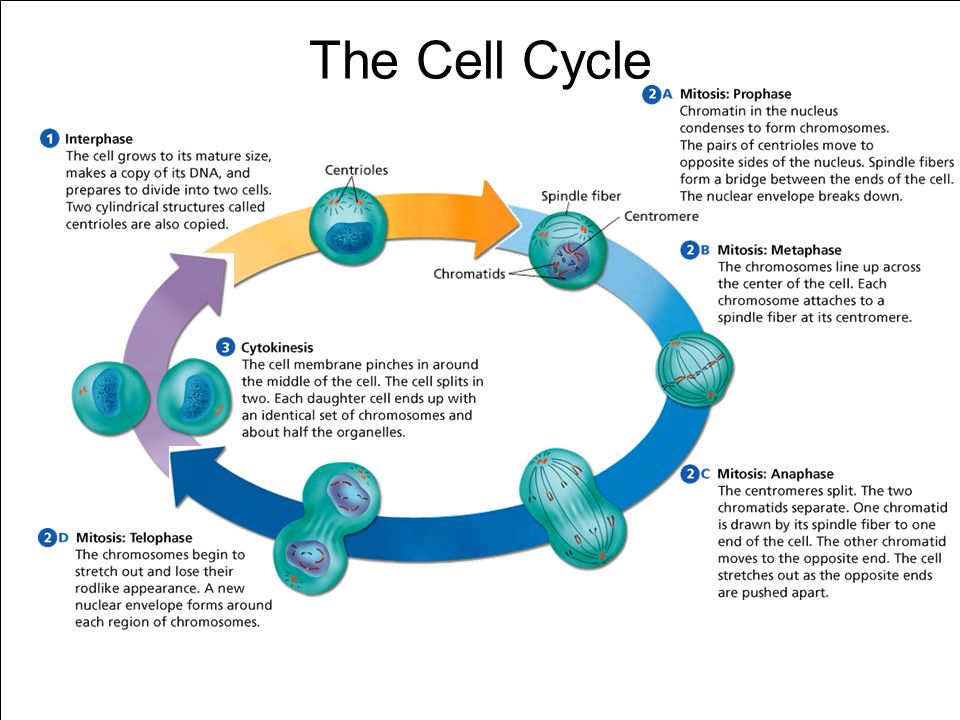
Cell Cycle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
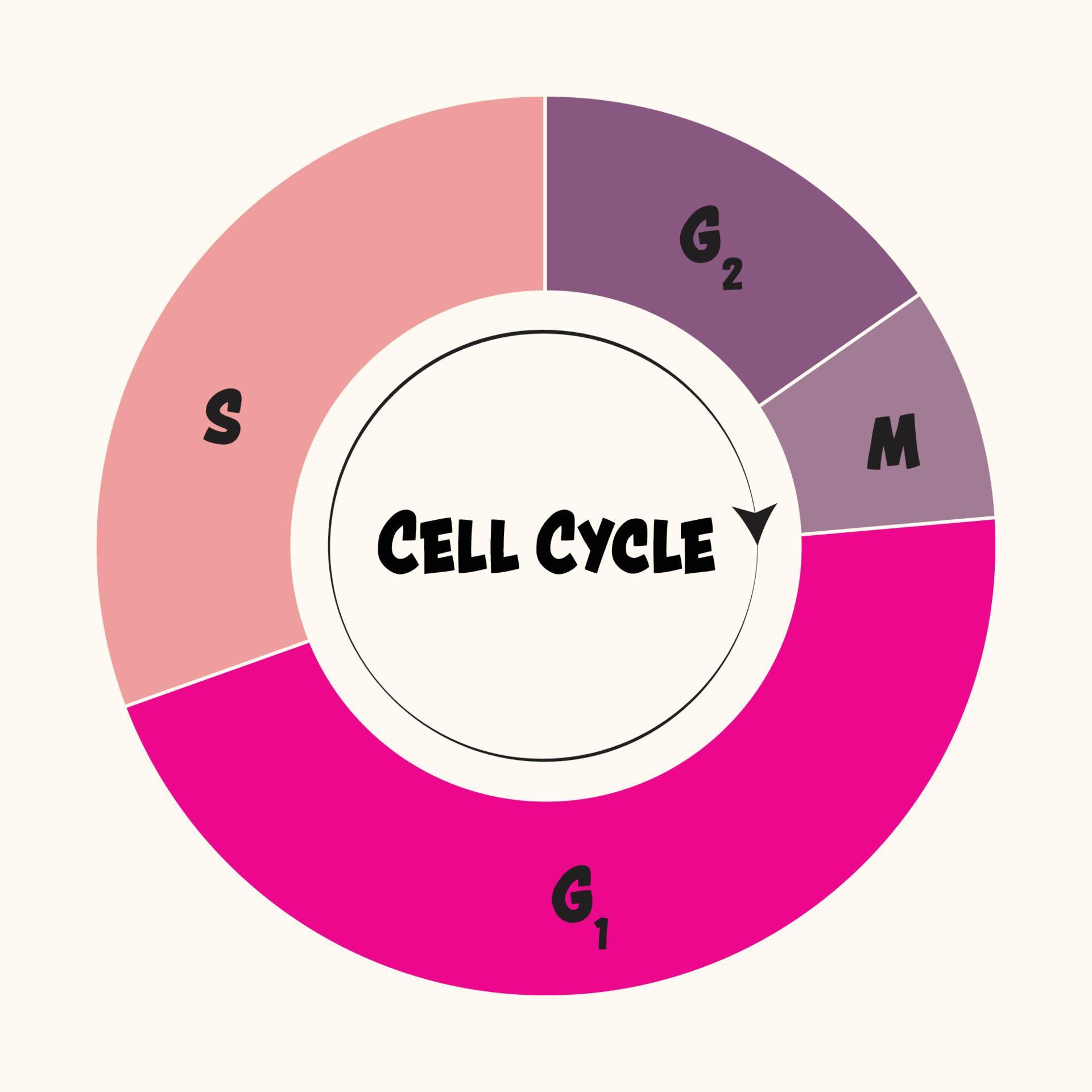
Phases of the cell cycle 6894530 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Web The Cell Cycle Is The Sequence Of Events Occurring In An Ordered Fashion Which Results In Cell Growth And Cell Division.
Interactive Radial Gene Expression Diagram For A Selected.
The G 1, S, And G 2 Phases.
What Is The Difference Between Stem Cells And Cancer Cells?
Related Post: