Draw Dna Replication, Web explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication;
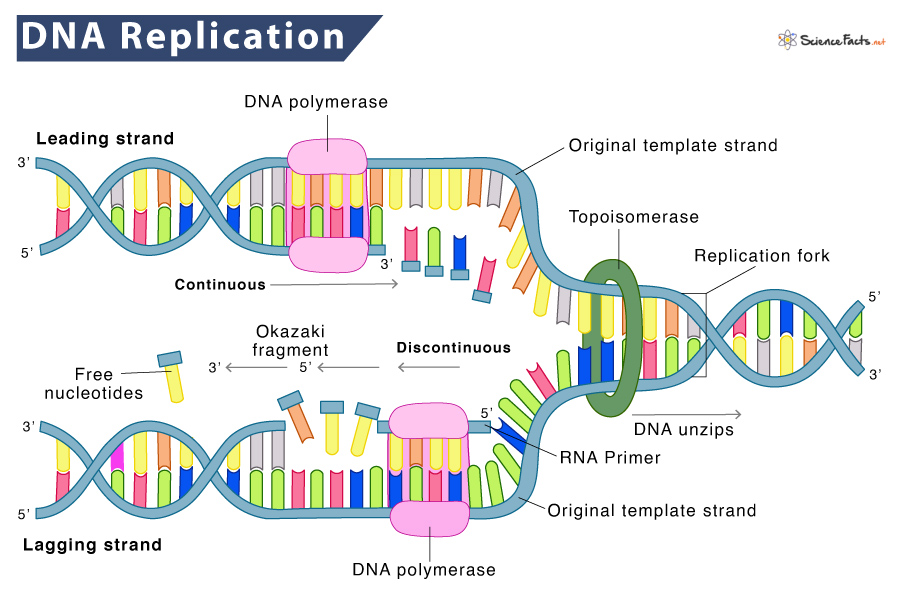
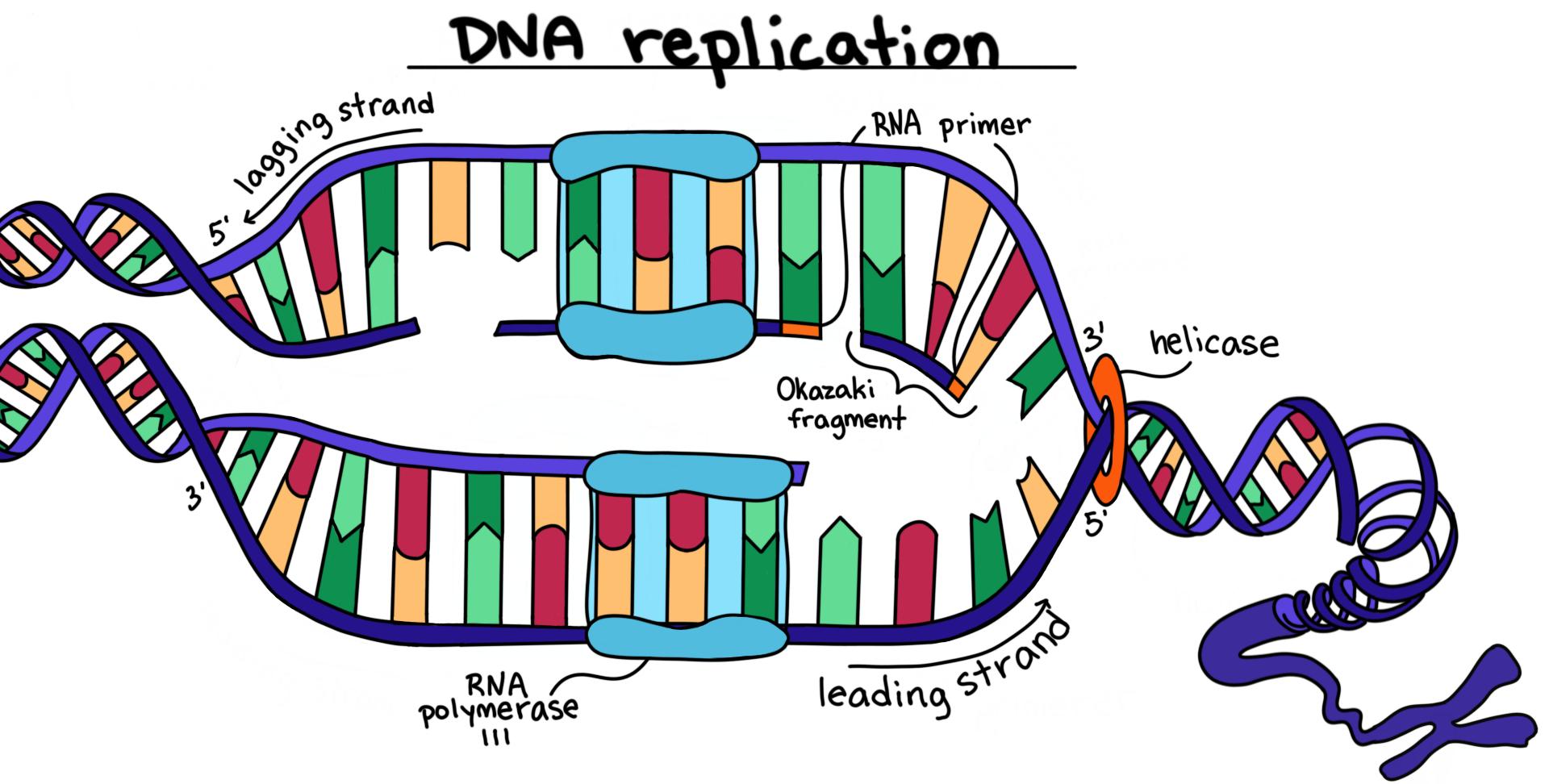
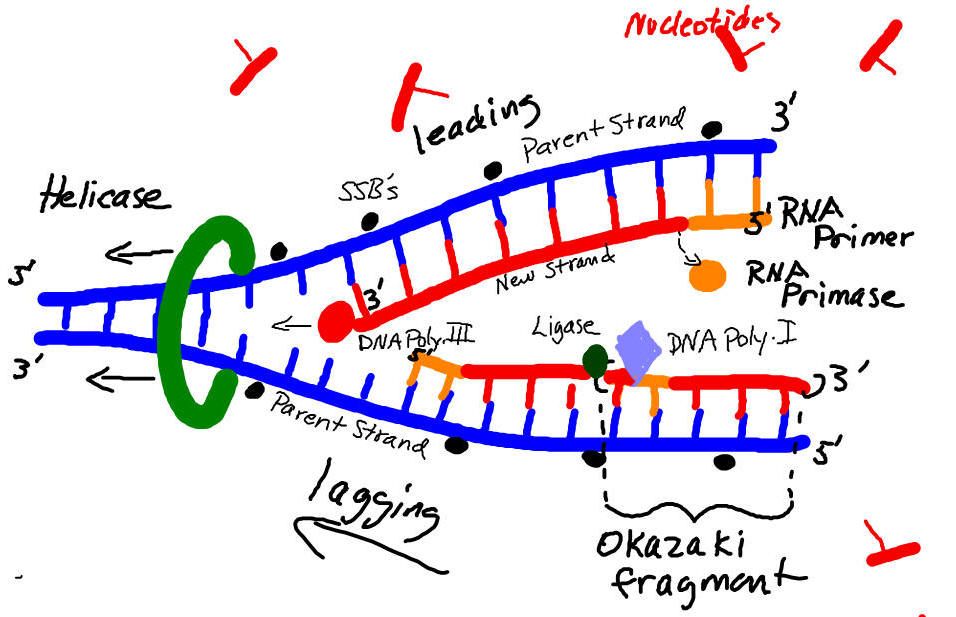
Draw Dna Replication - Web dna replication is a precise process where dna unwinds and splits into two strands. Web when a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the dna. Explore the dna replication process and roles of enzymes in eukaryotes and. We start by seeing the dna double helix being unzipped to form a. Therefore the main role of. Web basic features of dna replication: Each strand then serves as a template for a new dna molecule. Web explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Dna replication occurs in all living. Web dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. We start by seeing the dna double helix being unzipped to form a. Web in molecular biology, dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of dna from one original dna molecule. Let us first briefly consider the. Each strand then serves as a template for a new dna molecule. Dna synthesis is initiated at particular points. Therefore the main role of. Web dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of dna. A protein is one or more polymers of monomers called amino acids. Let us first briefly consider the. Leading and lagging strands and okazaki fragments. This is accomplished by the process of dna replication. Web dna polymers direct the production of other polymers called proteins. Web dna replication is a tightly controlled process that copies the genetic code, allowing its instructions to be conveyed from one generation of cells to the next. Web dna serves as the molecular basis of heredity through replication, expression, and. Be sure to follow the directionality. Web basic features of dna replication: All genetically relevant information of any dna molecule is present in its sequence of bases on two strands. Proteins are the workhorse molecules. Different proteins are also involved in the. Web dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of dna. A protein is one or more polymers of monomers called amino acids. Therefore the main role of. Different proteins are also involved in the. Web during dna replication, the enzyme helicase unwinds the dna double helix by disrupting the hydrogen bonds that keep it together. Cells do not live forever, and in light of this, they must pass their genetic information on to new cells, and be able to replicate the dna to be passed on to. Web explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Dna synthesis is initiated at particular points within the dna. Web basic features of dna replication: Leading and lagging strands. Let us first briefly consider the. Web dna replication starts by taking one dna molecule and giving two daughter molecules, with each newly synthesized molecule containing one new and one old. Web dna replication is the process in which a cell makes an identical copy of its dna. Web when a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell. Leading and lagging strands and okazaki fragments. Web dna replication is a tightly controlled process that copies the genetic code, allowing its instructions to be conveyed from one generation of cells to the next. These enzymes unzip dna molecules by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together. Web when a cell divides, it is important that each. We start by seeing the dna double helix being unzipped to form a. Web during dna replication, the enzyme helicase unwinds the dna double helix by disrupting the hydrogen bonds that keep it together. Be sure to follow the directionality. Explore the dna replication process and roles of enzymes in eukaryotes and. Web dna serves as the molecular basis of. These enzymes unzip dna molecules by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together. Web dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. It is vital for cell growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms as it helps with the. Therefore the main role of. Web dna replication is a tightly controlled process that copies the genetic code,. Web basic features of dna replication: Replication creates identical dna strands, while transcription. This is accomplished by the process of dna replication. Be sure to follow the directionality. Web dna replication is a complex process with many moving parts. Web explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand; Web when a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the dna. Web this 3d animation shows you how dna is copied by the cell, a process called dna replication. Dna replication occurs in all living. Web dna replication starts by taking one dna molecule and giving two daughter molecules, with each newly synthesized molecule containing one new and one old. Web dna polymers direct the production of other polymers called proteins. Web begin the process of dna replication by feeding the strands of the constructed dna into the top of the helicase enzyme on the replication mat. Leading and lagging strands and okazaki fragments. Let us first briefly consider the. A protein is one or more polymers of monomers called amino acids.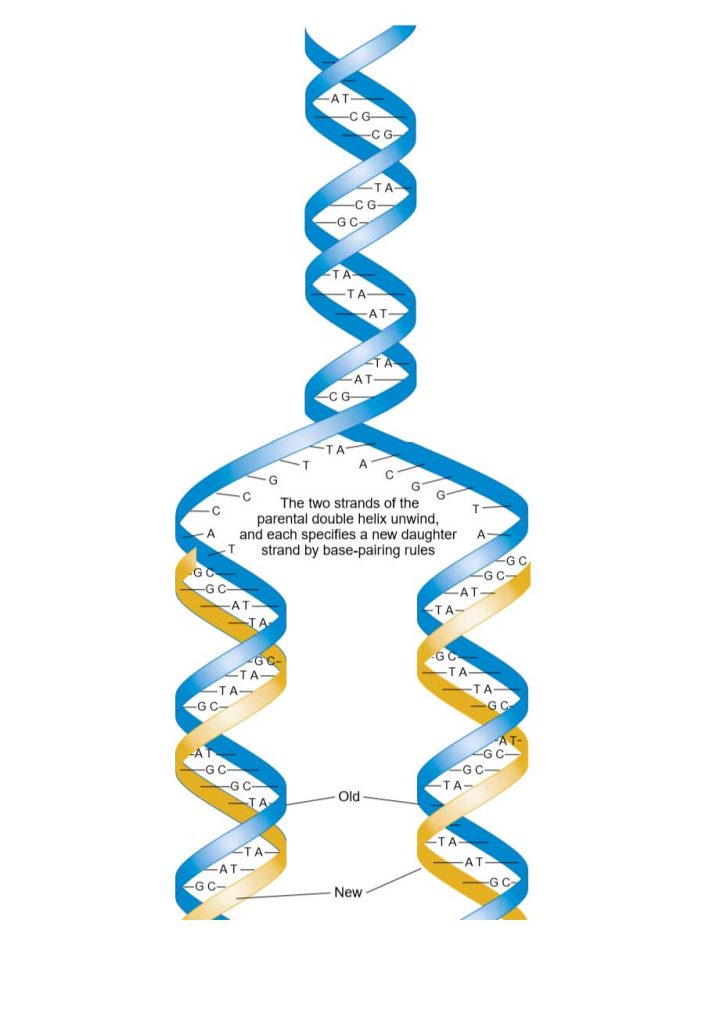
DNA Replication Study Solutions
DNA Replication Definition, Process, Steps, & Labeled Diagram

Diagram Explaining Dna Replication
Process of DNA Replication Expii
[Solved] Draw a diagram shows the replication steps remember that
Dna Replication Drawing Hot Sex Picture

Chapter 9 DNA Replication Chemistry

DNA Replication Structure Stages of Replication TeachMePhyiology

Cell Biology Glossary DNA Replication Draw It to Know It

Dna Replication Diagram With Labels
Each Strand Then Serves As A Template For A New Dna Molecule.
These Enzymes Unzip Dna Molecules By Breaking The Hydrogen Bonds That Hold The Two Strands Together.
Web In Molecular Biology, Dna Replication Is The Biological Process Of Producing Two Identical Replicas Of Dna From One Original Dna Molecule.
Web Dna Serves As The Molecular Basis Of Heredity Through Replication, Expression, And Translation Processes.
Related Post: