Cranial Drawer, Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture.
Cranial Drawer - Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured ccl can. Web the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) is responsible for the stability in the stifle joint and controls the cranial drawer movement, hyperextension and internal rotation. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. Web the cranial drawer test is diagnostic of cranial cruciate ligament injuries. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with positive. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. Autonomic neuropathy, and cranial mononeuropathies. Web diagnosis of partial cranial cruciate ligament (crcl) tears can be challenging for practitioners initially, but diagnosis is quite easy with a few basic questions, physical. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. Such a finding implies tearing primarily in the craniomedial band of the crcl because. Diagnosis is based on the demonstration of a specific test,. Web the cranial drawer test is diagnostic of cranial cruciate ligament injuries. Web the cranial drawer sign is pathognomonic for rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament (crcl). Find out the causes, signs, diagnosis and treatment options. A positive test result implies craniocaudal movement beyond the 0 mm to 2 mm mobility found in a. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. Web for the best diagnosis, you must seek the advice of a veterinarian. Your veterinarian holds the upper bone (femur) static and pulls the lower. Web diagnosis of partial cranial cruciate ligament (crcl) tears can be challenging for practitioners initially, but diagnosis is quite easy with a few basic questions, physical. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with positive.. Web the cranial drawer sign is pathognomonic for rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament (crcl). Web partial tears of the crcl often reveal cranial drawer instability only when the stifle is flexed. Web the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) is responsible for the stability in the stifle joint and controls the cranial drawer movement, hyperextension and internal rotation. Anesthesia may be. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. Web the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) is responsible for the stability in the stifle joint and controls the cranial drawer movement, hyperextension and internal rotation. Web learn about the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl), a ligament in the knee that can rupture and cause lameness in dogs. Web craniocaudal translation remains present. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. A positive test result implies craniocaudal movement beyond the 0 mm to 2 mm mobility found in a. Such a finding implies tearing primarily in the craniomedial band of the crcl. Find out the causes, signs, diagnosis and treatment options for. This abnormal forward movement of. A positive test result implies craniocaudal movement beyond the 0 mm to 2 mm mobility found in a. Web the clinical diagnosis is based on a positive drawer test in which the tibial plateau is manually displaced cranially with a fixed distal femur. Anesthesia may. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. Diagnosis is based on the demonstration of a specific test,. Your veterinarian holds the upper bone (femur) static and pulls the lower. Web the cranial drawer sign is pathognomonic for rupture of the cranial cruciate. Web learn about the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl), a ligament in the knee that can rupture and cause lameness in dogs. Web the cranial cruciate ligament (known as the anterior cruciate ligament or acl in people) is one of several ligaments in the stifle (knee) that connect the femur (thigh bone) to the. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive. Web close drawer menu open drawer menu menu. This laxity or looseness between the tibia and the femur cannot exist if the. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with positive. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. Find out the causes, signs, diagnosis and treatment options for. Web the key to diagnosis of a ruptured ccl is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called the 'cranial drawer sign'. Web the cranial cruciate ligament (ccl) is responsible for the stability in the stifle joint and controls the cranial drawer movement, hyperextension and internal rotation. Web the clinical diagnosis is based on a positive drawer test in which the tibial plateau is manually displaced cranially with a fixed distal femur. Web the other test is the cranial drawer test. In some cases, however, a crisp endpoint to the cranial drawer motion and a. Web partial tears of the crcl often reveal cranial drawer instability only when the stifle is flexed. Web close drawer menu open drawer menu menu. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured ccl can. Web the cranial drawer test is diagnostic of cranial cruciate ligament injuries. Diagnosis is based on the demonstration of a specific test,. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. Autonomic neuropathy, and cranial mononeuropathies. Web a specific manipulation during the exam is performed to elicit stifle laxity (cranial drawer motion). Web craniocaudal translation remains present under passive manipulation (cranial drawer test) and is possible with sufficient anterior shear loading.
4 Tips To The Perfect Dog Brace Cast Hero Blog
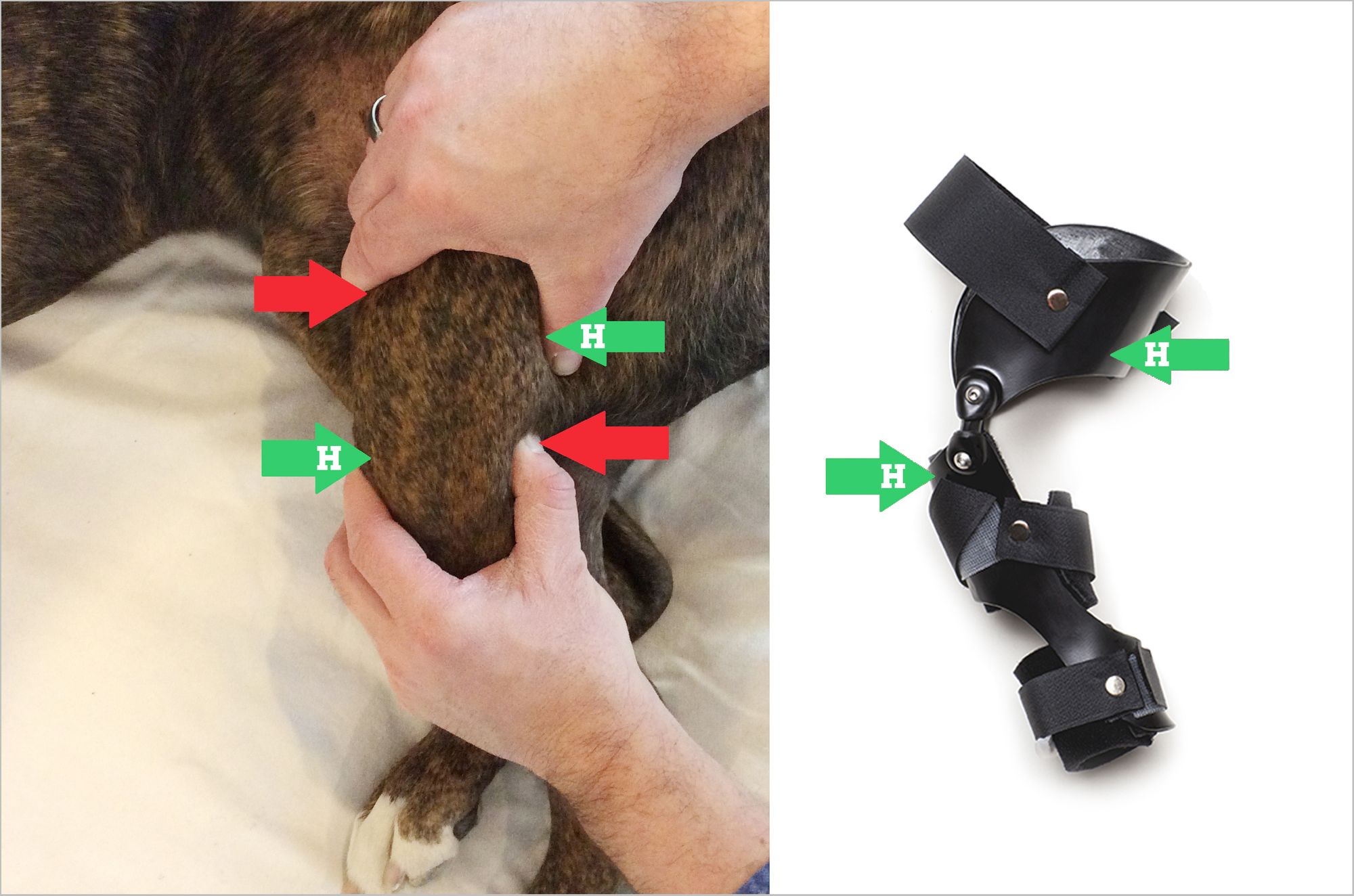
Torn ACL in Dogs How Braces Help

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior

Medicine Notes, Emergency Medicine, Physical Therapy Education, Nurse
![]()
Anatomical landmarks and corresponding reference systems. LE Lateral

Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament

Dog with Cranial Drawer YouTube

Tibial Thrust Vs Cranial Drawer Drawing.rjuuc.edu.np

Positive Cranial Drawer Movement is diagnostic for a torn Cranial
Web During The Lameness Examination, Your Veterinarian Will Try To Demonstrate A Particular Movement, Called A Cranial Or Anterior Drawer Sign.
A Positive Test Result Implies Craniocaudal Movement Beyond The 0 Mm To 2 Mm Mobility Found In A.
This Laxity Or Looseness Between The Tibia And The Femur Cannot Exist If The.
Web Diagnosis Of Cranial Cruciate Ligament (Ccl) Tears Is Made Through A Combination Of Orthopedic Examination Findings (Eg, Positive Cranial Drawer, Cranial Tibial Translation).
Related Post: