Anatomical Position Drawing, In the anatomical position, the body is upright, directly facing the observer, feet flat and directed forward.
Anatomical Position Drawing - It is not reliant on whether the patient is standing, supine, prone, sitting, etc. It is used to describe the location and relationship of body parts to one another. Web anatomical position is the description of any region or part of the body in a specific stance. The upper limbs are held out to each side of the body, and the palms of the hands face forward. Practice drawing your figure in different poses and different angles. Mastering the art of body pose drawing requires an understanding of human anatomy and proportion, as well as practice and persistence. Each provides essential reference points and functions for medical procedures and communication. Web just like paper maps are oriented with north at the top of the page, the standardized anatomical view of the body is its position standing upright with the feet at shoulder width and parallel and toes facing forward. Web draw simple shapes to give to the body, following typical human body proportions. In this position, the lower margins of the orbitals (eye sockets), the lower margin of the orbits, and the upper margins of the ear canals (poria) lie in the same horizontal plane. In the supine position, a patient lies horizontally on their back, with their face and upper body facing up, while in the prone position, a patient. Web gesture drawing is a great way to understand the human form and how proportions of the body distort due to unique poses and positions. The upper limbs are held out to each side. These two people are both in anatomical position. Web drawing body poses is an essential skill for artists, as it helps them accurately capture the human figure and convey emotions and actions through their artwork. The location of body parts and associated pathology can be difficult to describe without specific anatomical terminology. Web gesture drawing is a great way to. Web learn anatomy as you browse our collection of colorful, large and clearly labeled human body diagrams. These two people are both in anatomical position. For example, would you like a pose that other artists are not using? Web how to draw anatomy step by step. In the anatomical position, the body is upright, directly facing the observer, feet flat. Practice drawing your figure in different poses and different angles. It is important to understand that not all standing positions can be considered anatomical. In the supine position, a patient lies horizontally on their back, with their face and upper body facing up, while in the prone position, a patient. The key to improving your drawings is to do your. Web draw simple shapes to give to the body, following typical human body proportions. Web learn anatomy as you browse our collection of colorful, large and clearly labeled human body diagrams. Learn to create expressive drawings of human anatomy by exploring abstraction and movement. The upper limbs are held out to each side of the body, and the palms of. Web the anatomical position of the skull is the frankfurt plane. [updated to correct inferior/posterior error in original. For example, would you like a pose that other artists are not using? Web gesture drawing is a great way to understand the human form and how proportions of the body distort due to unique poses and positions. Web how to draw. These two people are both in anatomical position. Building the muscle structure and anatomy on top of those shapes. Learn to create expressive drawings of human anatomy by exploring abstraction and movement. Practice drawing your figure in different poses and different angles. Web the anatomical position of the skull is the frankfurt plane. For teachers, students, health professionals, or anyone interested in learning about the anatomy of the human body. Mastering the art of body pose drawing requires an understanding of human anatomy and proportion, as well as practice and persistence. In this position, the lower margins of the orbitals (eye sockets), the lower margin of the orbits, and the upper margins of. Learn to create expressive drawings of human anatomy by exploring abstraction and movement. Anatomy is a challenging subject, but i hope that this article can be a quick guide for you and get you in the mood to keep learning. Mastering the art of body pose drawing requires an understanding of human anatomy and proportion, as well as practice and. Sorting is a great way to find what you want. The legs are parallel, with feet flat on the floor and facing forward. Web learn anatomy as you browse our collection of colorful, large and clearly labeled human body diagrams. The universal descriptions allow for a standardised reference point for referring to structures, which provides precision and reduces room for. Consider how each move would affect the rest of the body’s movement. It is important to understand that not all standing positions can be considered anatomical. Mastering the art of body pose drawing requires an understanding of human anatomy and proportion, as well as practice and persistence. Anatomy is a challenging subject, but i hope that this article can be a quick guide for you and get you in the mood to keep learning. Web standard anatomical position (or the standard reference position) of the body is defined as the human being standing upright, with feet together, arms by the side of his body and none of his long bones crossing each other.the face is looking forwards, mouth closed with a neutral facial expression.the arms are slightly externally rotated at the s. Building the muscle structure and anatomy on top of those shapes. Use the my lists button. The human figure step by step. The universal descriptions allow for a standardised reference point for referring to structures, which provides precision and reduces room for medical error or ambiguity. In the anatomical position, the body is upright, directly facing the observer, feet flat and directed forward. Map the muscle structures you’ve studied onto your figure’s shape. For example, would you like a pose that other artists are not using? Practice drawing your figure in different poses and different angles. Standard anatomical positions are used to standardise the position of appendages of animals with respect to the main body of the organism. In the anatomical position, the body is upright, directly facing the observer, feet flat and directed forward. It is not reliant on whether the patient is standing, supine, prone, sitting, etc.
Anatomical References Human body Systems Organs A Rescuer

Anatomical Terminology Body Planes, Positions & Sections Video

Anatomical Position Drawing at GetDrawings Free download

Anatomical Position, Planes, and sections Shanta Anatomy& Physiology

How To Draw A Body Step By Step / Proportions And Form How To Draw The

Blank Anatomical Position Diagram / Standard Anatomical Position
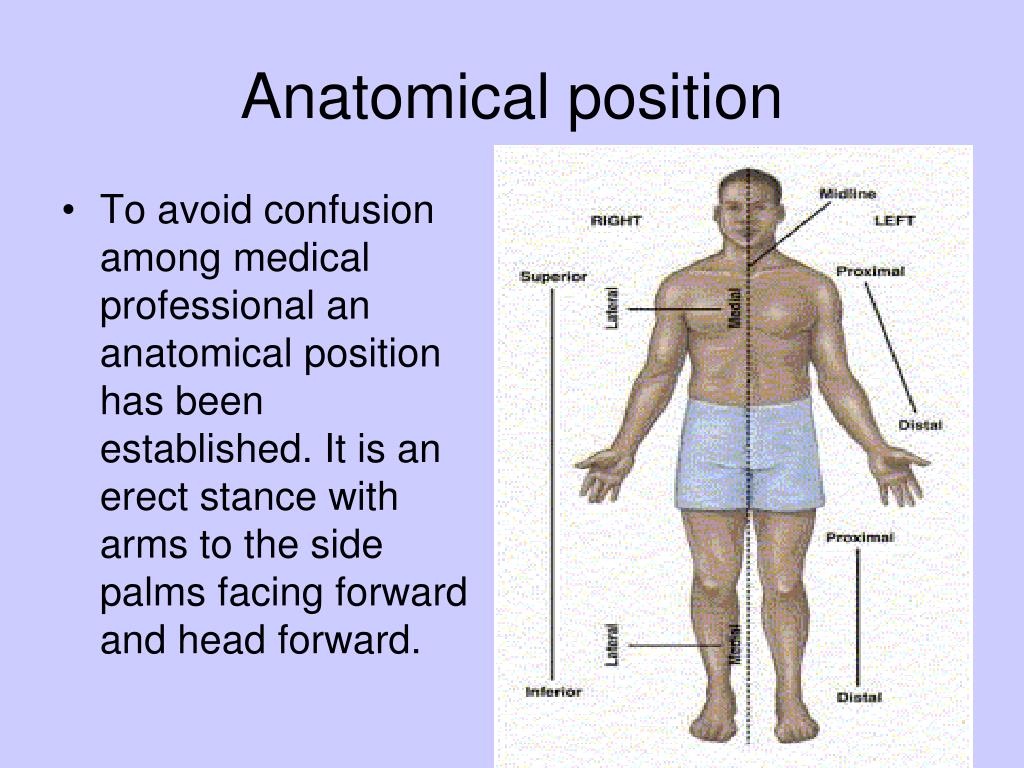
anatomical positions and directions

Gross Anatomy Glossary Anatomical Orientation Draw It to Know It

Learning drawing principles Human anatomy drawing, Anatomy drawing
Hand Drawn Illustration of Different Human Body Positions Stock Vector
This Standard Position (Standing Straight, Looking Forward, Arms At Your Side, And Facing Forward) Keeps Everyone On The Same Page When You’re Talking Anatomy And Physiology.
Web This Free A&P Lesson Plan Contains Short Activities In Human Anatomy Atlas 2020 To Help Students Visualize Anatomical Planes, Positions, And Directional Terms!
Web The Main Anatomical Positions Are Supine, Prone, Right Lateral Recumbent, And Left Lateral Recumbent;
Web The Anatomical Position Is The Standard Reference Position For The Human Body.
Related Post: