Anaphase Drawing, The stage before anaphase, metaphase, the chromosomes are pulled to the metaphase plate, in the middle of the cell.
Anaphase Drawing - Web anaphase is the fourth phase of mitosis, which is a process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two, identical daughter cells. Web generally, anaphase i involve separating the chromosomes from each sister chromatid to the opposite poles still attached to the microtubules of the cell while anaphase 2 involves the actual split of the sister chromatids into single chromatids. Humans have 46) but the diagrams below show mitosis of an animal cell with only four chromosomes, for simplicity. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. At the end of anaphase, each pole contains a complete compilation of chromosomes. Web model anaphase by removing the white beads (centromere) from the sister chromatids to separate and move them toward opposite poles of the cell. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of. The process of mitosis is significant in both cell division as well as cell reproduction. Centrosomes and microtubules play pivotal roles in orchestrating this complex process, ensuring the successful replication of cells. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During anaphase, the chromosomes that are lined up in the center of the cell are pulled apart, separating the sister chromatids. Web generally, anaphase i involve separating the chromosomes from each sister chromatid to the opposite poles still attached to the microtubules of the cell while anaphase 2 involves the actual split of the sister chromatids into single chromatids. Web. In meiosis i, cells go through four phases: Web anaphase is a stage during eukaryotic cell division in which the chromosomes are segregated to opposite poles of the cell. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The process continues until late anaphase at which time the chromosomes have segregated to the poles in the eventual daughter cells. Centrosomes and microtubules play pivotal. These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During anaphase, the chromosomes that are lined up in the center of the cell are pulled apart, separating the sister chromatids. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web anaphase i is the third stage of meiosis i and follows. Prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The process of mitosis is significant in both cell division as well as cell reproduction. During anaphase, the chromosomes that are lined up in the center of the cell are pulled apart, separating the sister chromatids. Web anaphase is a stage during eukaryotic cell division in which the. Centrosomes and microtubules play pivotal roles in orchestrating this complex process, ensuring the successful replication of cells. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. The chromatids only start separating when the pressure is sufficient to split the centromere. Web this is a drawing of anaphase and a real photomicrograph of a cell in anaphase. After separation at the. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web this is a drawing of anaphase and a real photomicrograph of a cell in anaphase. During anaphase, the chromosomes that are lined up in the center of the cell are pulled apart, separating the sister chromatids. Web during anaphase, the sister chromatids at the equatorial plane are split apart at the centromere. Web anaphase is the fourth phase of mitosis, which is a process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of. You can learn more about these stages in the video on mitosis. Web anaphase is a stage during eukaryotic cell division in which the chromosomes are segregated to opposite poles of the cell. Web mitosis consists of five morphologically distinct phases: Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During anaphase, the chromosomes that are lined up in the center of the cell are pulled apart, separating the sister chromatids. The process of mitosis is significant in both cell division as well as cell reproduction. Web anaphase, in mitosis and meiosis, the stage of cell division in which separated chromatids (or homologous [like] chromosome. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Web anaphase, in mitosis and meiosis, the stage of cell division in which separated chromatids (or homologous [like] chromosome pairs, as in the first meiotic division) move toward the opposite poles of the spindle apparatus. Web model anaphase by removing the white beads (centromere) from the sister chromatids. Prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The chromatids only start separating when the pressure is sufficient to split the centromere. Prophase i, metaphase i, anaphase i, and telophase i. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web mitosis takes place in four stages: Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). The process continues until late anaphase at which time the chromosomes have segregated to the poles in the eventual daughter cells. Web model anaphase by removing the white beads (centromere) from the sister chromatids to separate and move them toward opposite poles of the cell. Web anaphase is the third phase of mitosis. Web anaphase i is the third stage of meiosis i and follows prophase i and metaphase i. Centrosomes and microtubules play pivotal roles in orchestrating this complex process, ensuring the successful replication of cells. During prophase i, chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, creating more variation. Spindle fibers not connected to chromatids lengthen and elongate the cell. Most organisms contain many chromosomes in the nuclei of their cells (eg. Web generally, anaphase i involve separating the chromosomes from each sister chromatid to the opposite poles still attached to the microtubules of the cell while anaphase 2 involves the actual split of the sister chromatids into single chromatids. After separation at the centromere, the chromatids are now called chromosomes.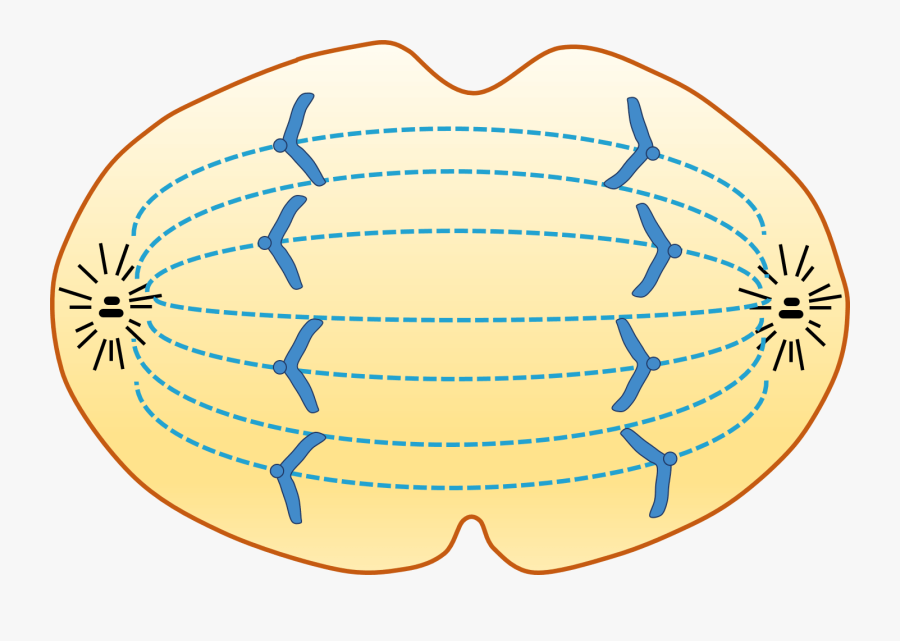
Anaphase Diagram , Free Transparent Clipart ClipartKey

Meiosis Anaphase Free Images at vector clip art online
Anaphase Illustrations Illustrations, RoyaltyFree Vector Graphics
/meiosis_anaphase_1-56a09b4c5f9b58eba4b2052b.jpg)
What Is Anaphase in Cell Biology?
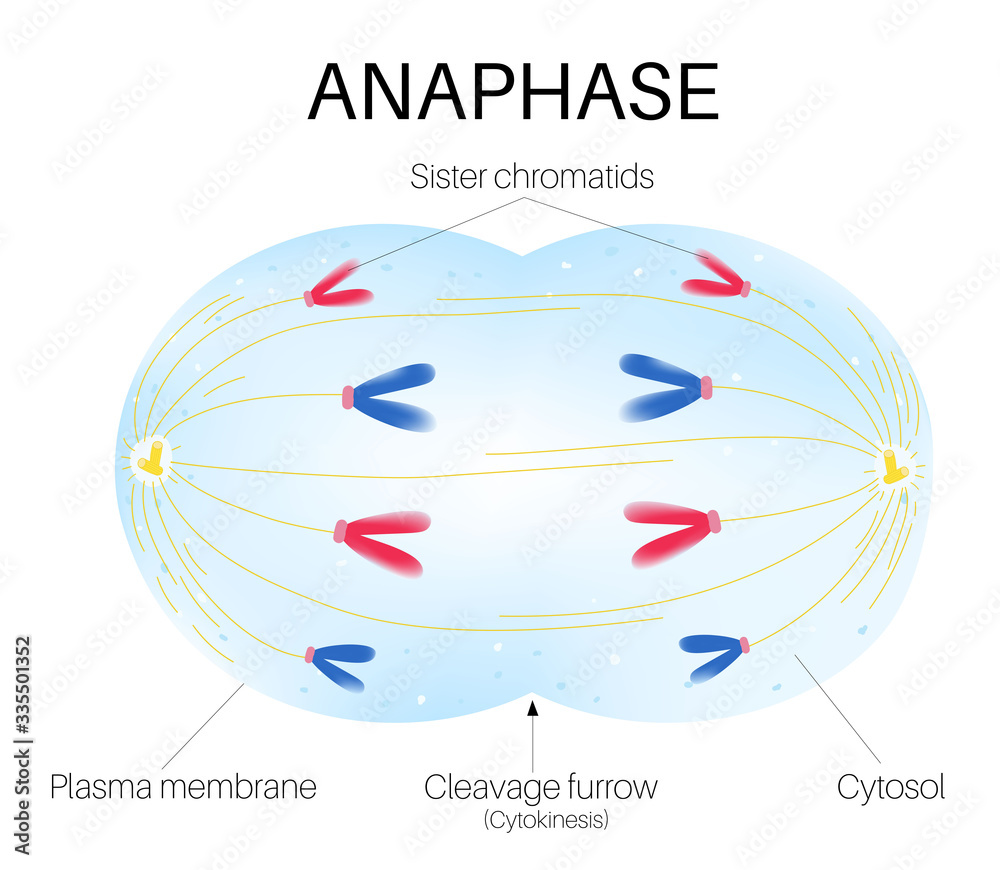
Anaphase is the phase of the cell cycle Stock Vector Adobe Stock
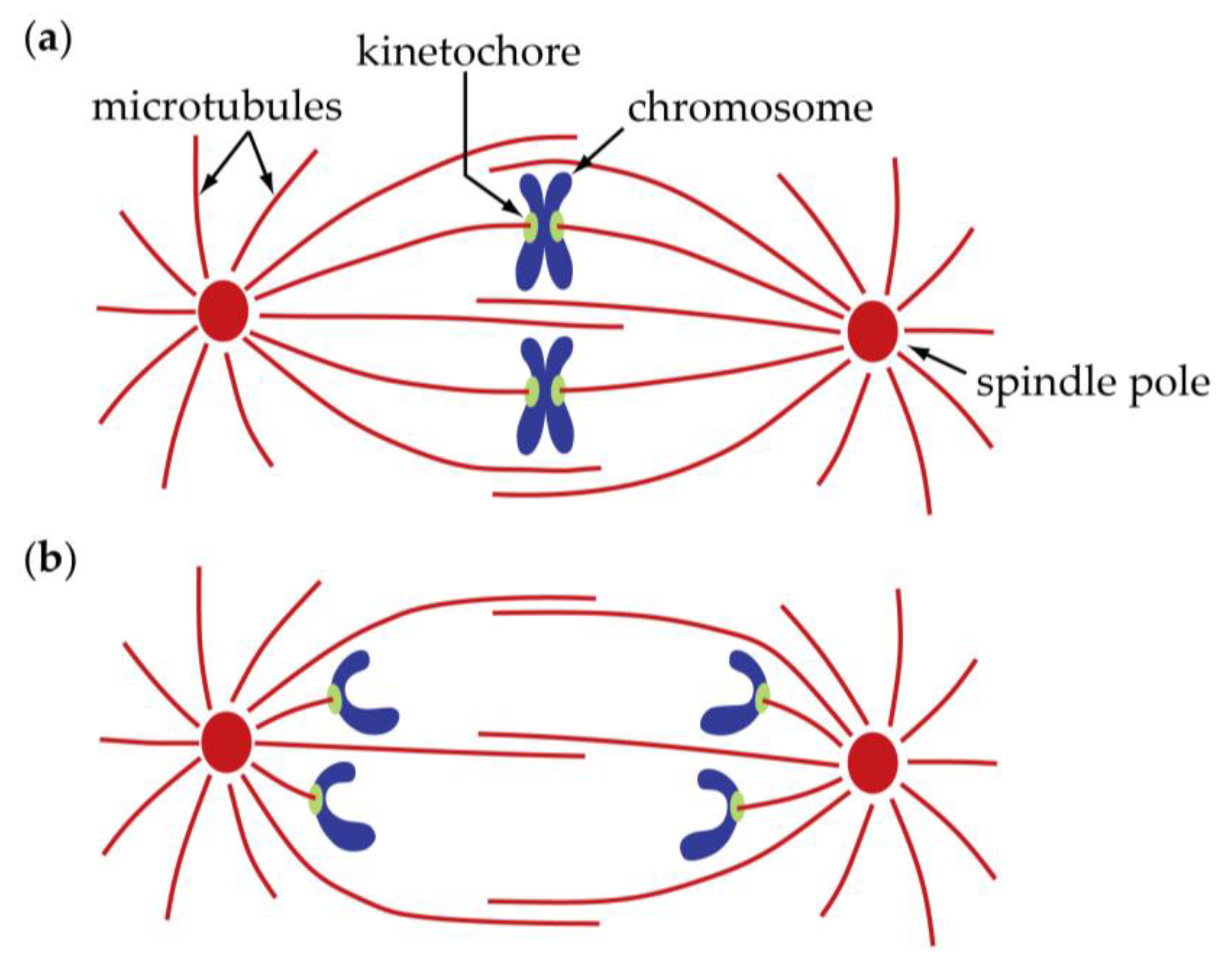
Biology Free FullText Anaphase A Disassembling Microtubules Move

Anaphase is stage of cell division. 15274241 Vector Art at Vecteezy

Anaphase — Definition & Diagrams Expii

9+ which diagram represents anaphase i of meiosis YenyukLilia

Anaphase stage of mitosis 8576777 Vector Art at Vecteezy
It Starts As Soon As Metaphase Ends, And It Comes Right Before Telophase.
The Process Of Mitosis Is Significant In Both Cell Division As Well As Cell Reproduction.
These Phases Are Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, And Telophase.
In Meiosis I, Cells Go Through Four Phases:
Related Post:
